Как умное производство улучшает контроль допусков при обработке на ЧПУ?
Интеллектуальное производство объединяет автоматизацию, анализ данных и цифровые системы обратной связи, чтобы повысить эффективность на каждом этапе процесса механической обработки. Связывание станков, датчиков и систем контроля качества позволяет инженерам обеспечивать стабильный контроль допусков, снижая при этом количество переделок и отходов.
Мониторинг и обратная связь в реальном времени
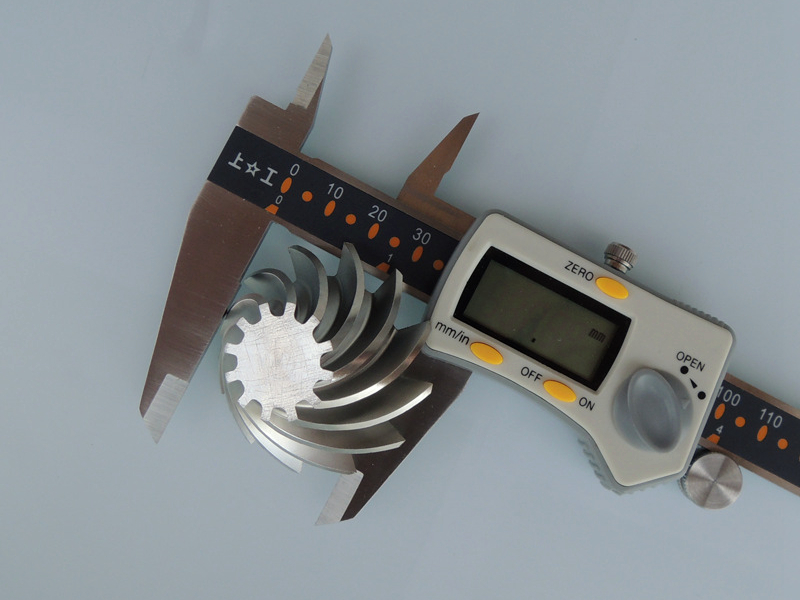
Современные платформы ЧПУ-обработки, оснащённые умными датчиками, постоянно собирают данные о нагрузке на шпиндель, вибрациях и температуре. Эти показатели анализируются для коррекции траекторий инструмента и скоростей резания в реальном времени, что поддерживает стабильность размеров даже при динамических нагрузках. Например, системы многоосевой обработки могут автоматически компенсировать прогиб или тепловое смещение, обеспечивая неизменную точность на сложных поверхностях. Такая система с замкнутым циклом особенно ценна при прецизионной обработке и электроэрозионной обработке (EDM), где часто требуются допуски до ±0,005 мм. Результатом становится меньшая зависимость от ручных измерений и повышенная повторяемость при серийном производстве.
Цифровой двойник и предиктивное управление процессом
Интеллектуальное производство использует технологию цифрового двойника — виртуальные модели, отражающие физический процесс обработки. Инженеры могут моделировать износ инструмента, распределение тепла и поведение материала до начала фактической обработки. При обработке сложных материалов, таких как Inconel 718 или Ti-6Al-4V, эти симуляции помогают оптимизировать траектории инструмента и предсказывать возможные отклонения размеров при определённых условиях резания. Системы предиктивного обслуживания также обеспечивают калибровку критически важных станков, используемых при шлифовании на ЧПУ или высокоскоростном фрезеровании. Предвидя износ инструмента и биение шпинделя, интеллектуальные системы управления уменьшают дрейф допусков и поддерживают соответствие деталей спецификациям на протяжении всего производственного цикла.
Автоматизированный контроль и управление качеством на основе данных
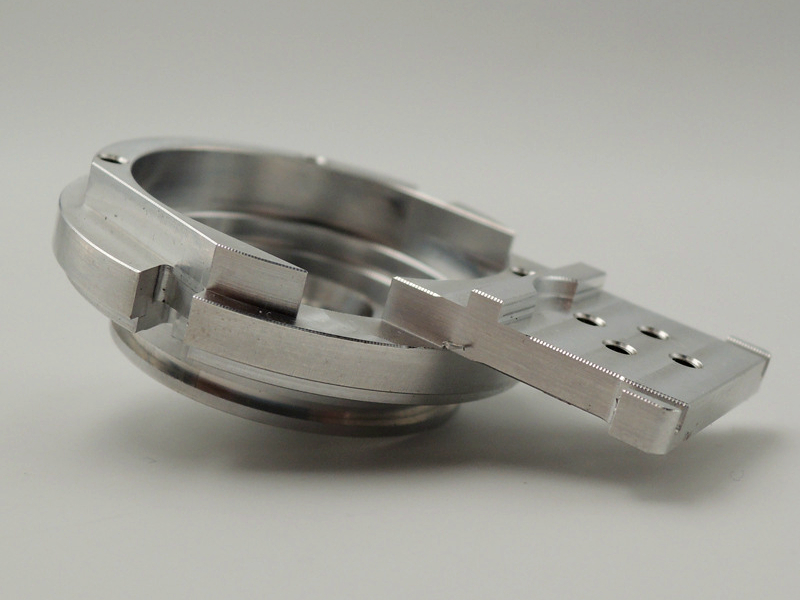
Высокоточные детали проверяются с помощью встроенной метрологии — зондирования, лазерного сканирования и оптических измерений. При интеграции с прототипированием на ЧПУ или малообъёмным производством эти системы выявляют отклонения до того, как они станут дефектами. Собранные размерные данные автоматически сравниваются с моделями GD&T для подтверждения геометрической точности. Целостность поверхности также контролируется через автоматизированные системы финишной обработки. Такие процессы, как полировка деталей ЧПУ или нитрирование, выполняются с одинаковыми параметрами с использованием роботизированных ячеек, что гарантирует соответствие микрошероховатости строгим требованиям по допускам поверхности.
Интеграция материалов и отраслей
Эффективность контроля допусков зависит не только от интеллекта оборудования, но и от поведения используемых материалов. Алюминиевые сплавы, такие как алюминий 7075 и алюминий 6061-T6, выигрывают от адаптивной оптимизации скоростей, минимизирующей коробление. Для высокотехнологичных отраслей, таких как авиация, медицинское оборудование и автомобилестроение, мониторинг в реальном времени гарантирует, что каждый компонент сохраняет точность даже при длительных циклах обработки и изменчивости материалов.
Результат: выше точность, ниже стоимость
Благодаря интеграции интеллектуальных систем управления производители достигают большей точности допусков при меньшем количестве проверок и отходов. Прослеживаемость процессов и цифровая документация поддерживают непрерывное совершенствование во всей производственной цепочке. Таким образом, интеллектуальное производство превращает контроль допусков из ручного процесса в автоматизированную, проверяемую данными систему, которая стабильно соответствует самым строгим отраслевым стандартам.