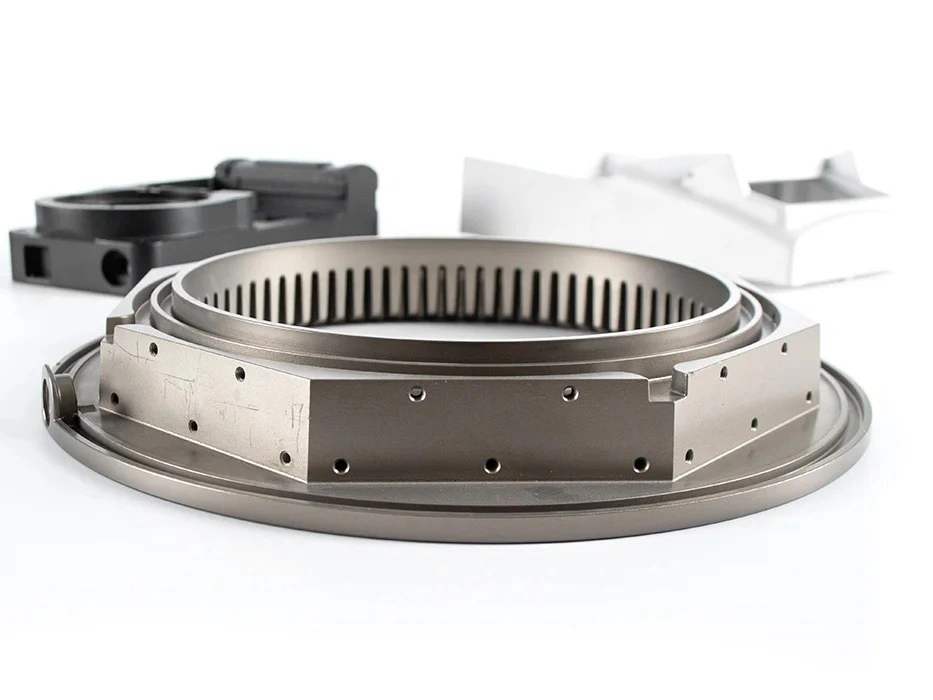
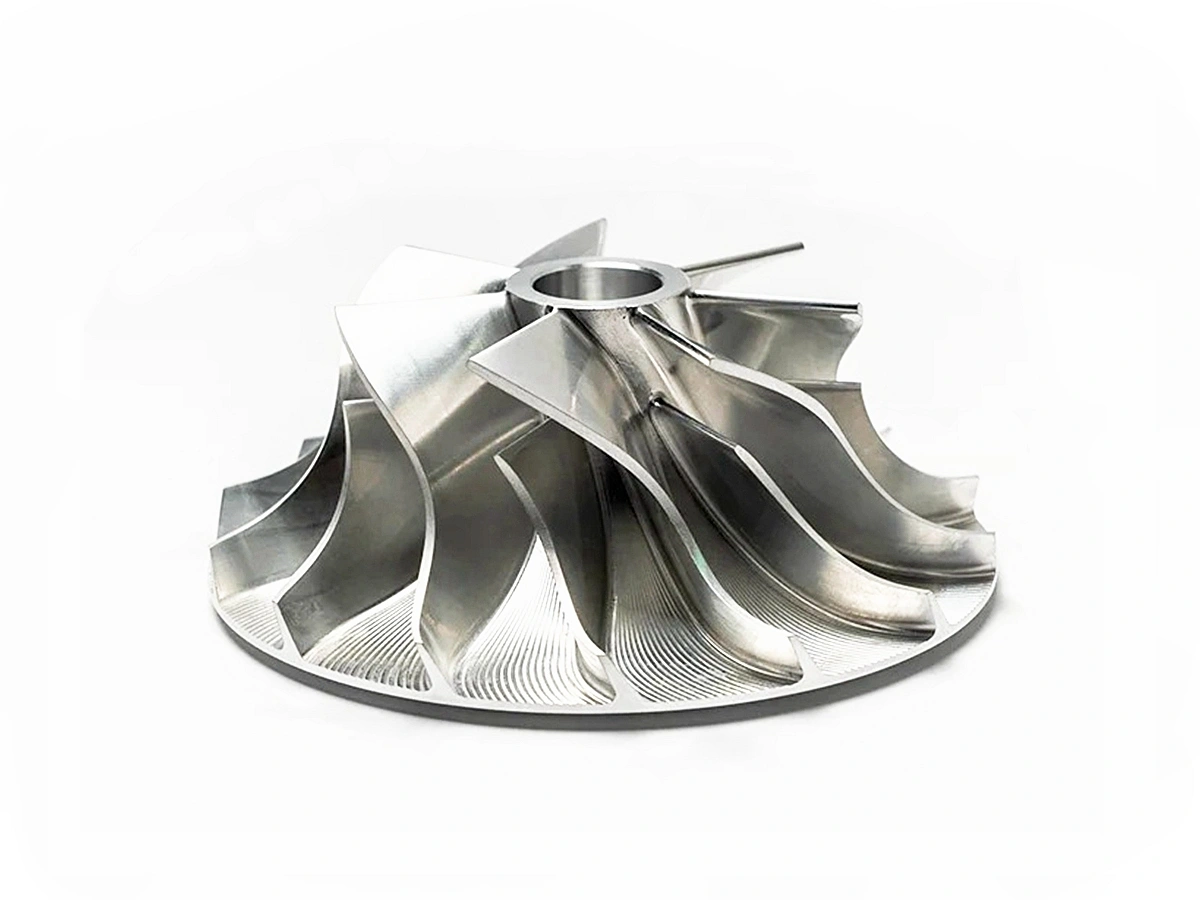
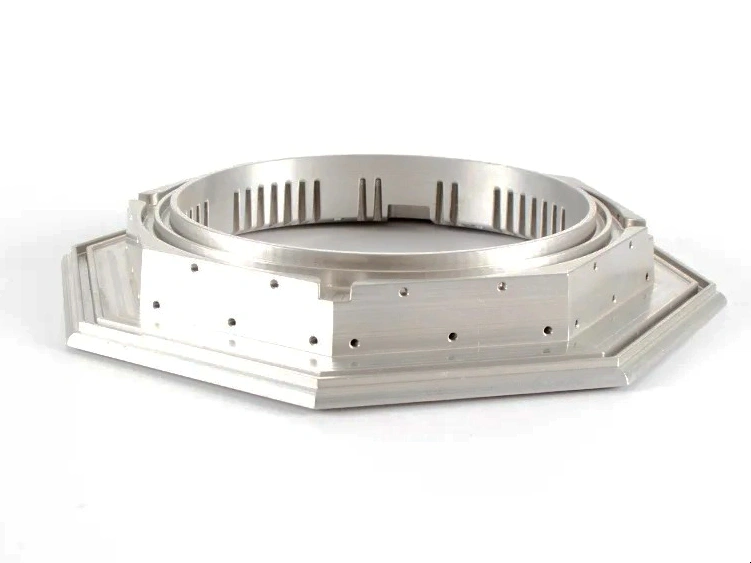
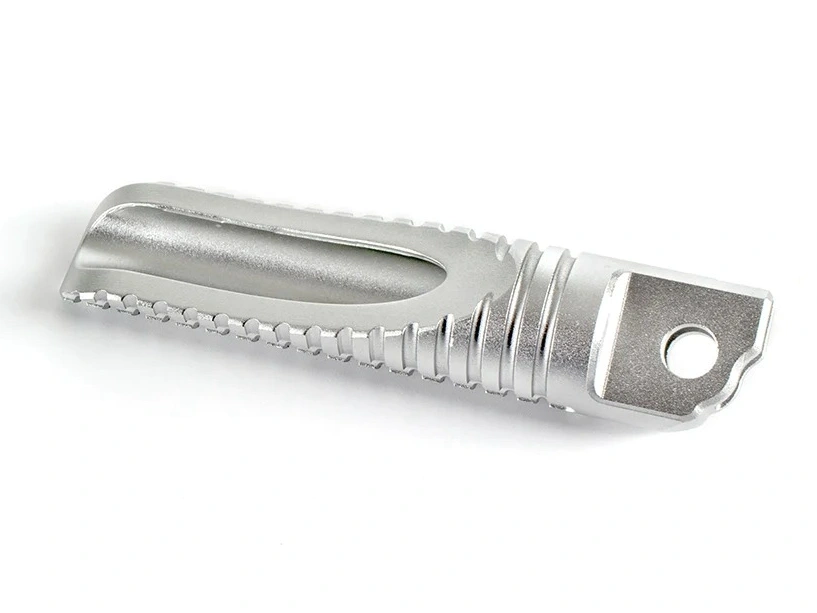
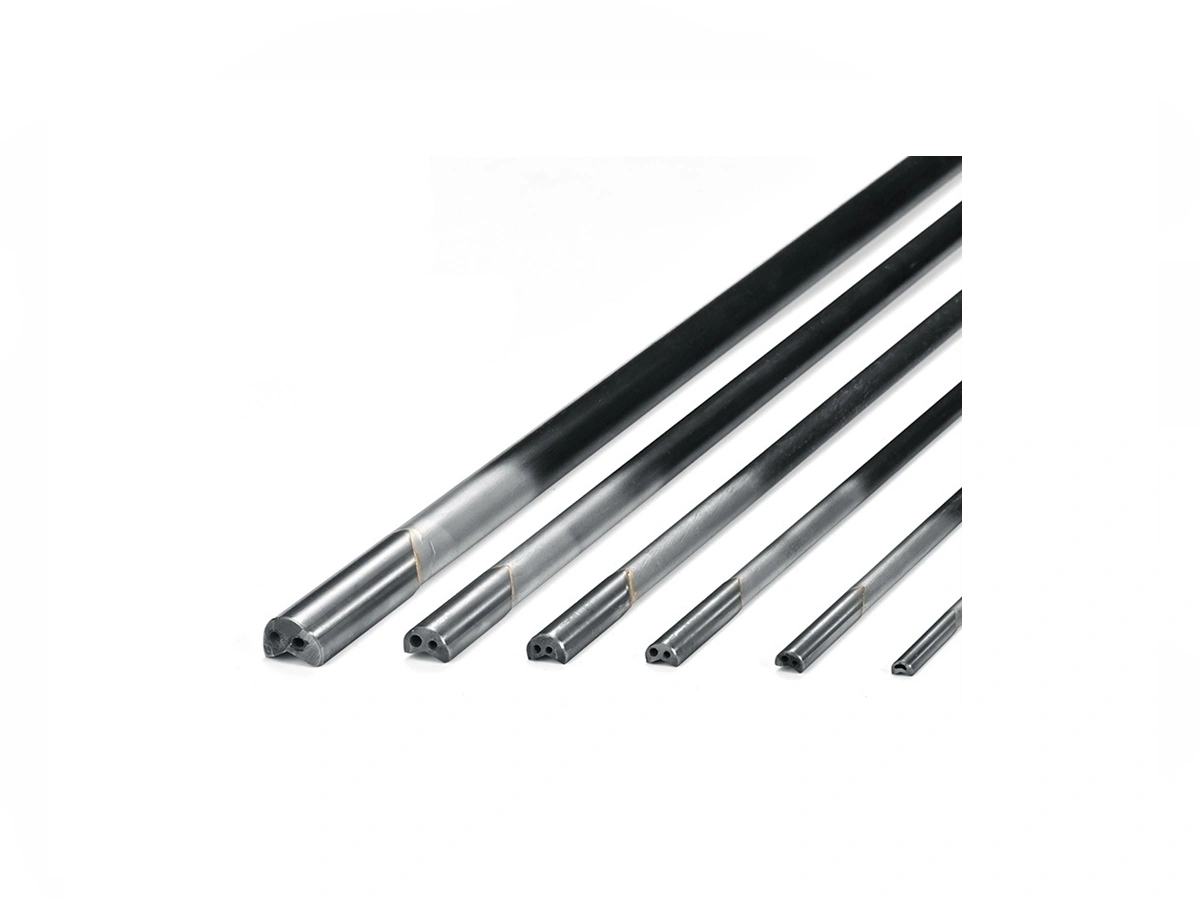
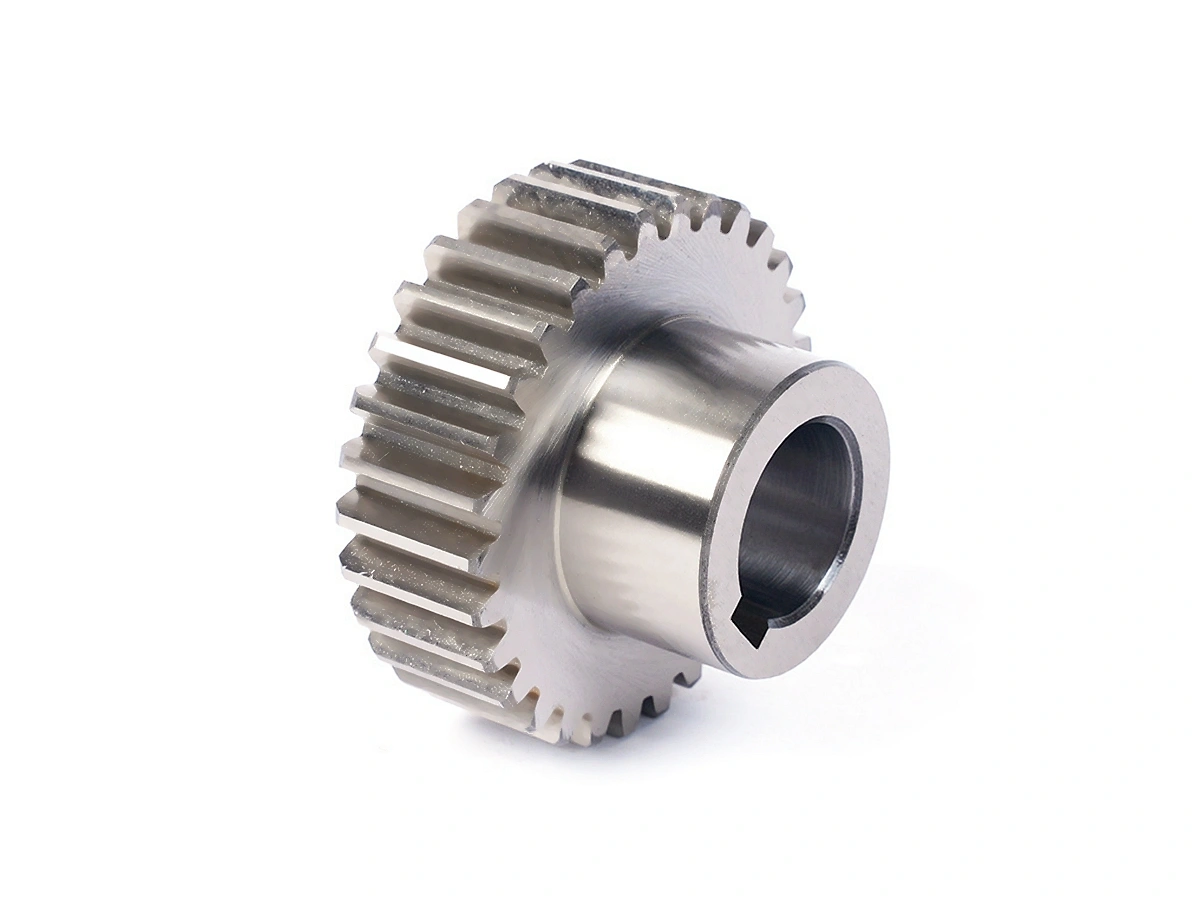
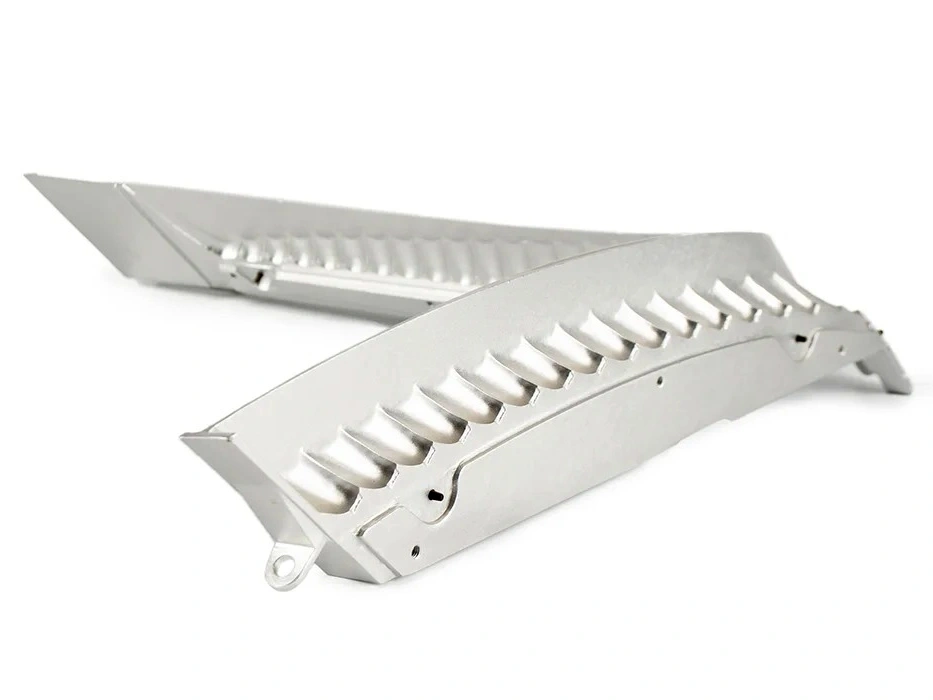
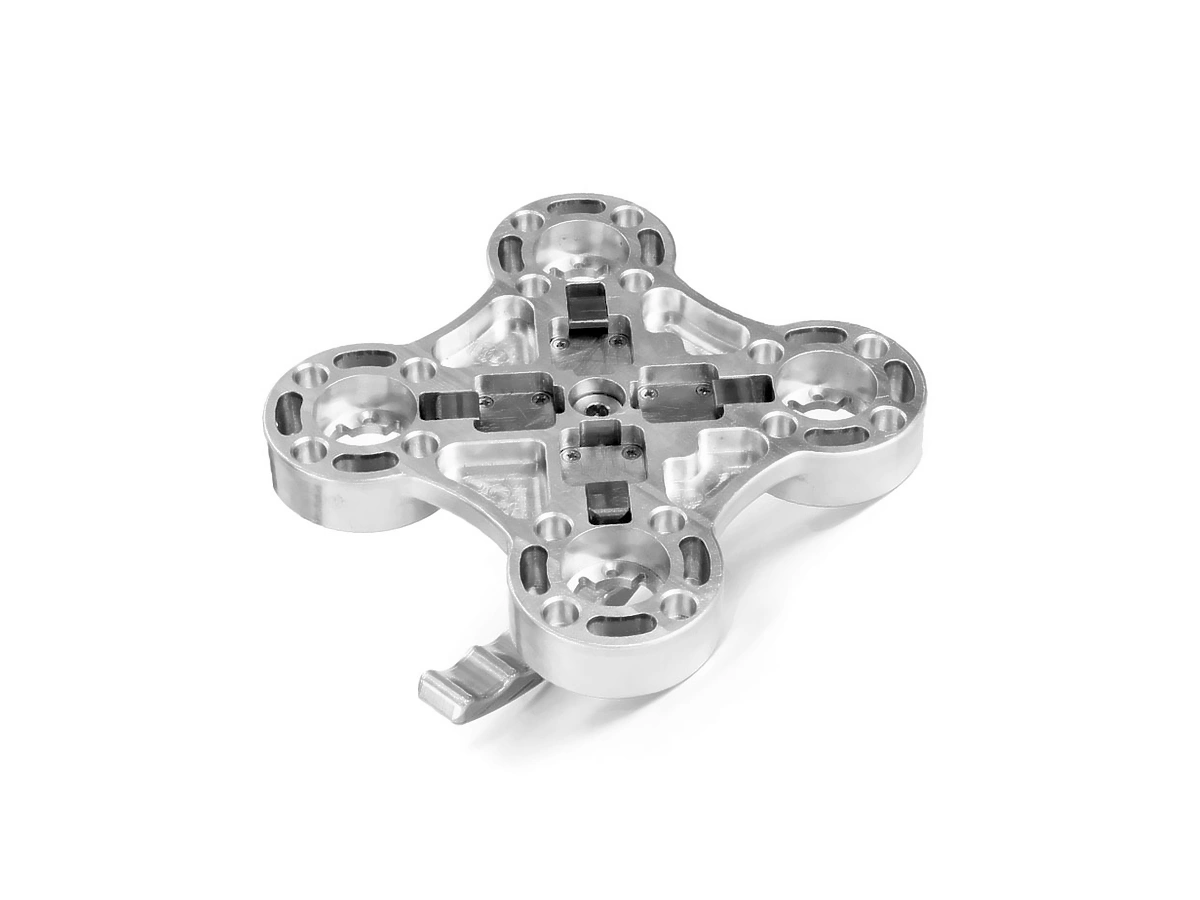
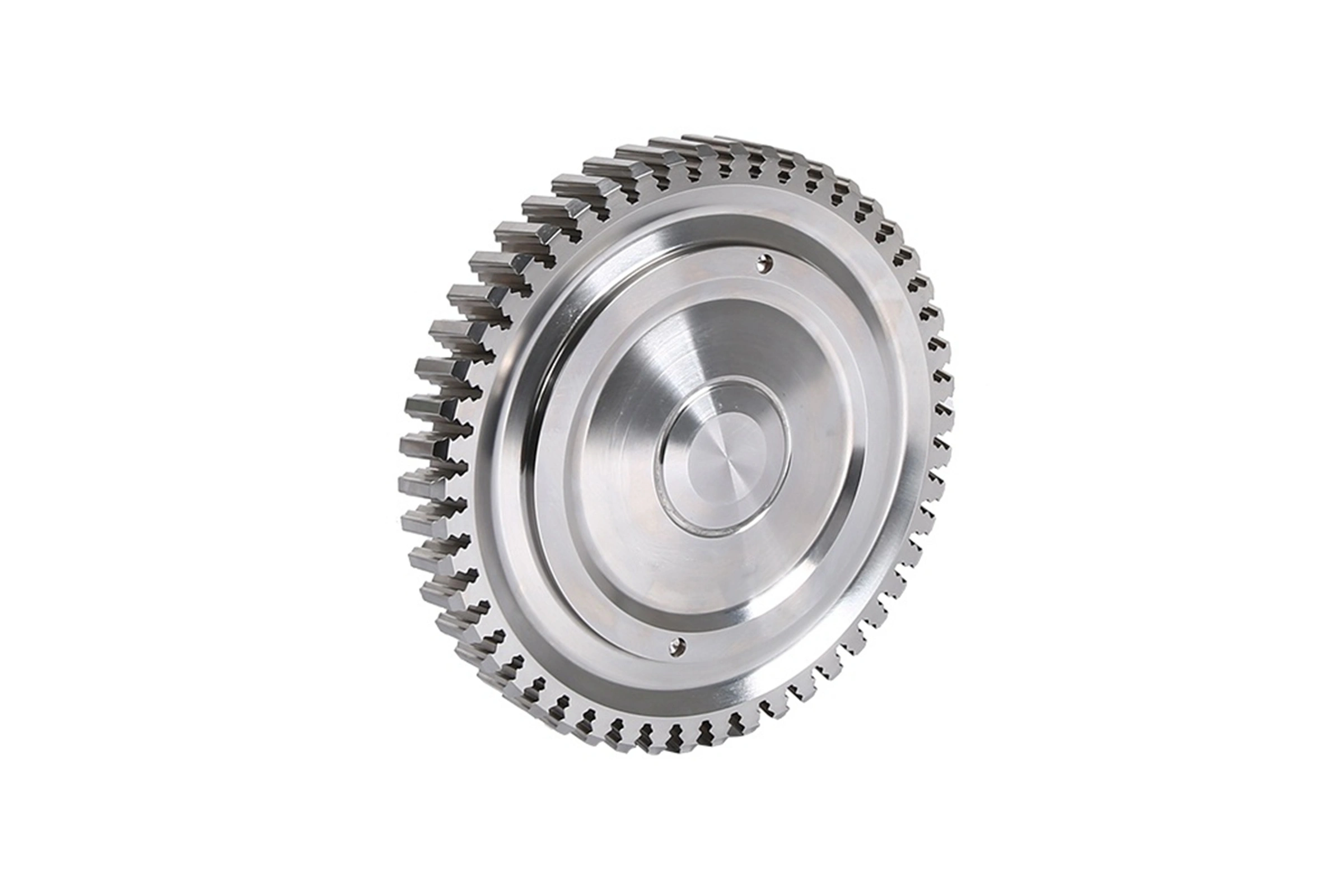
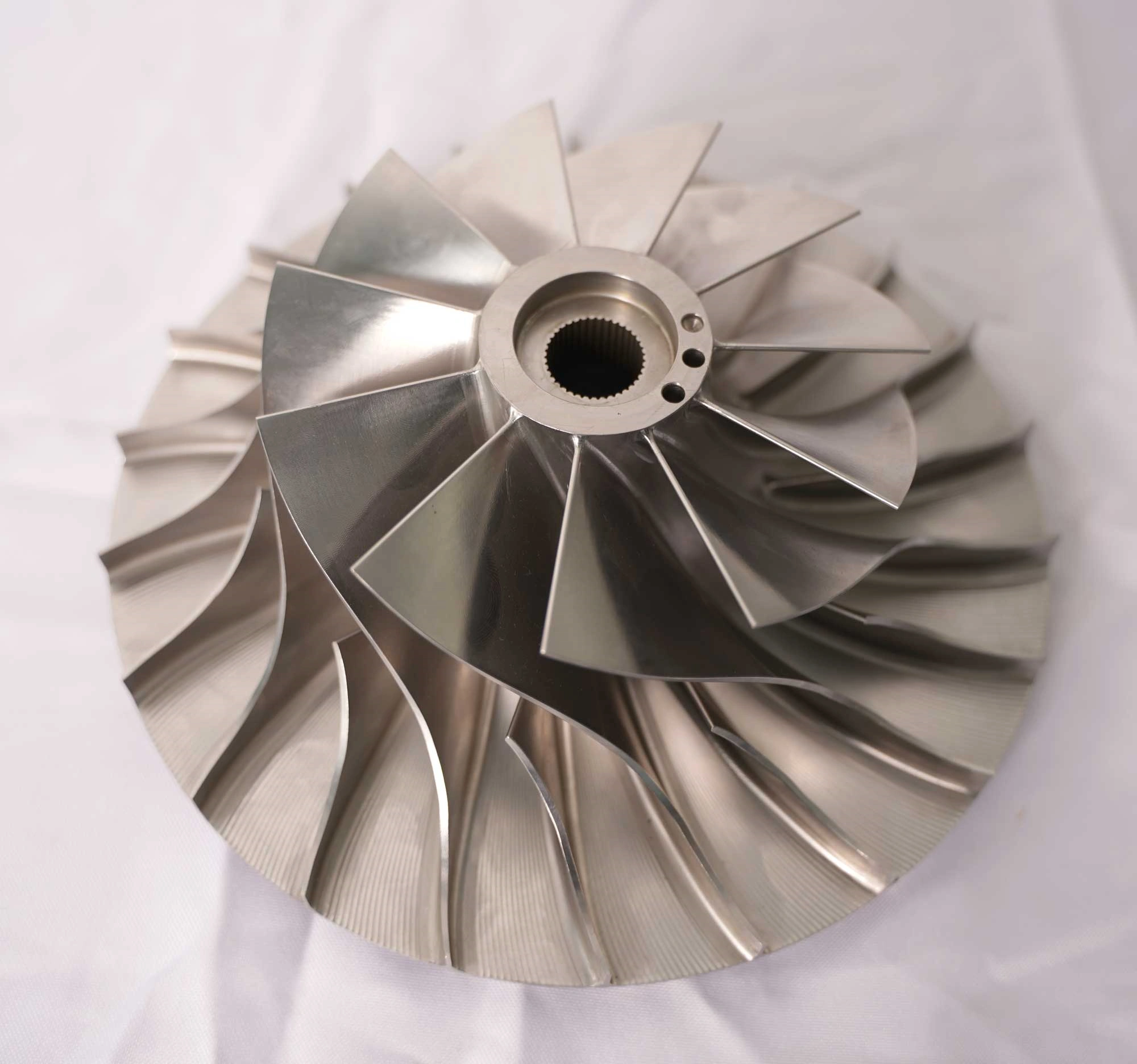
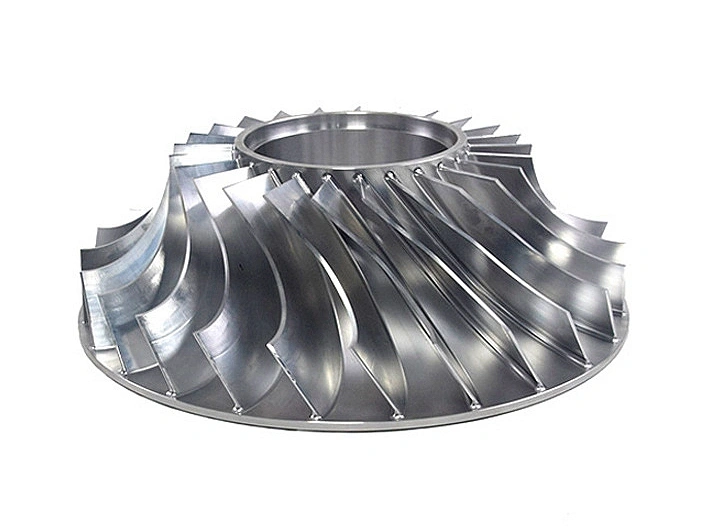
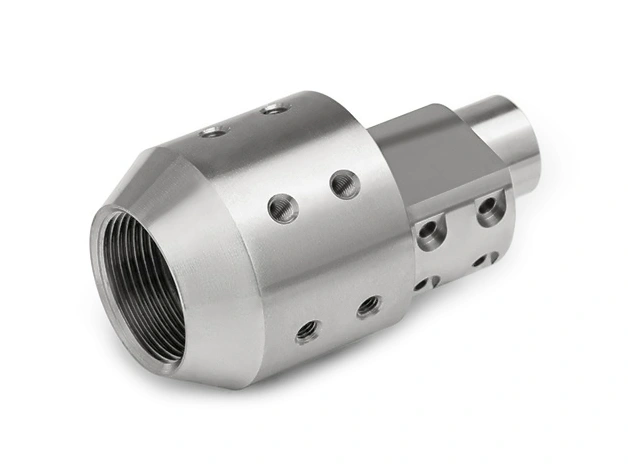
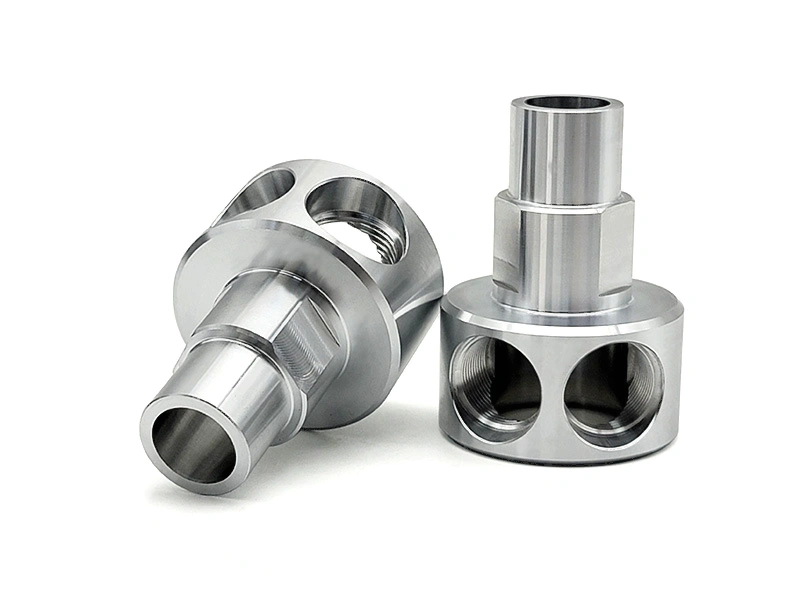
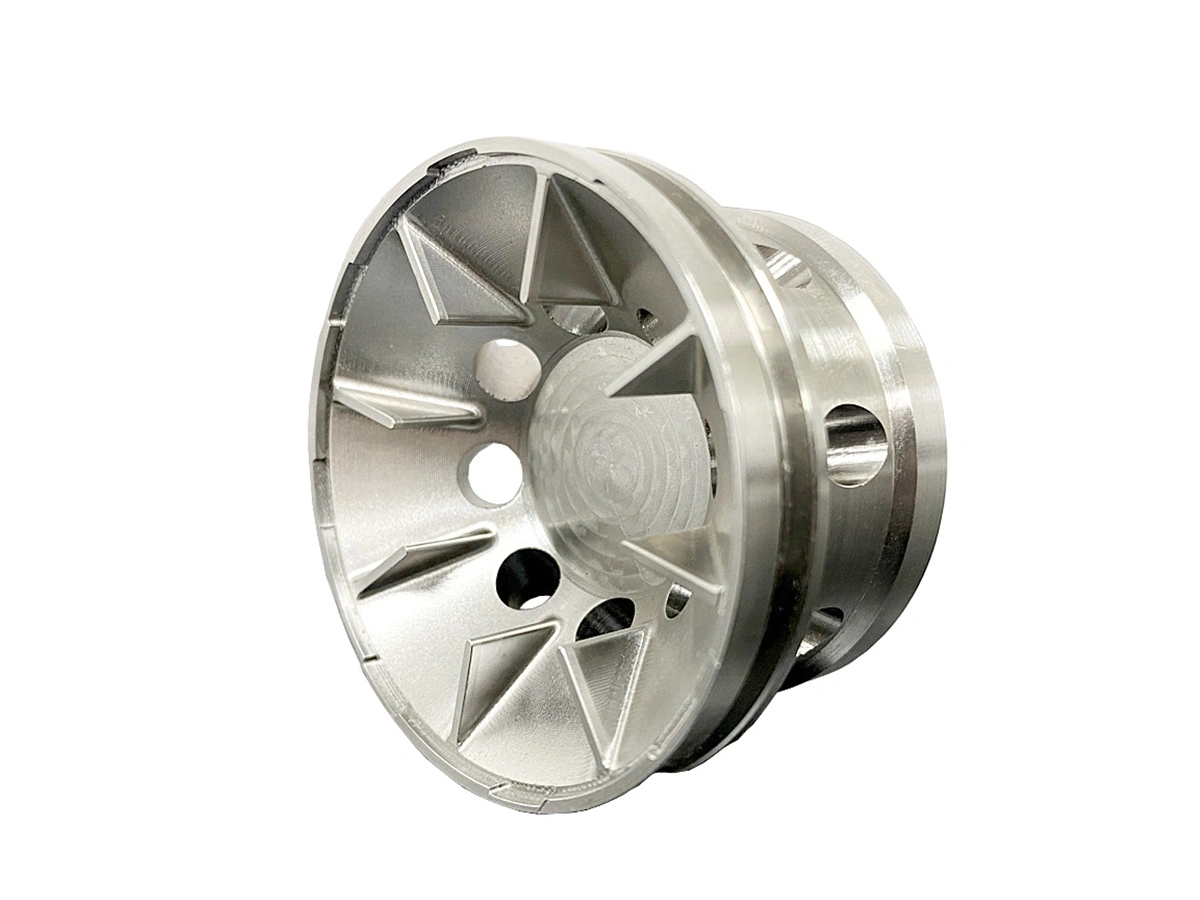
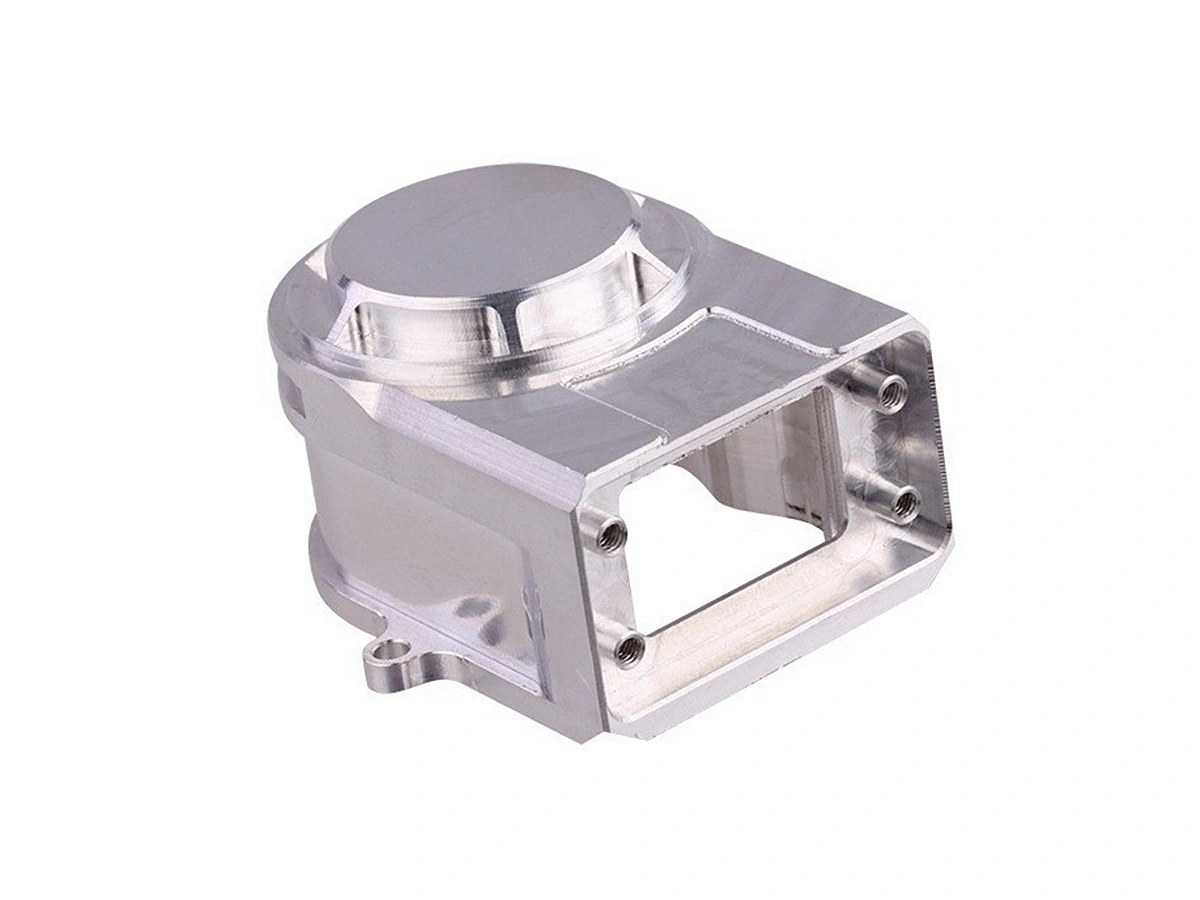
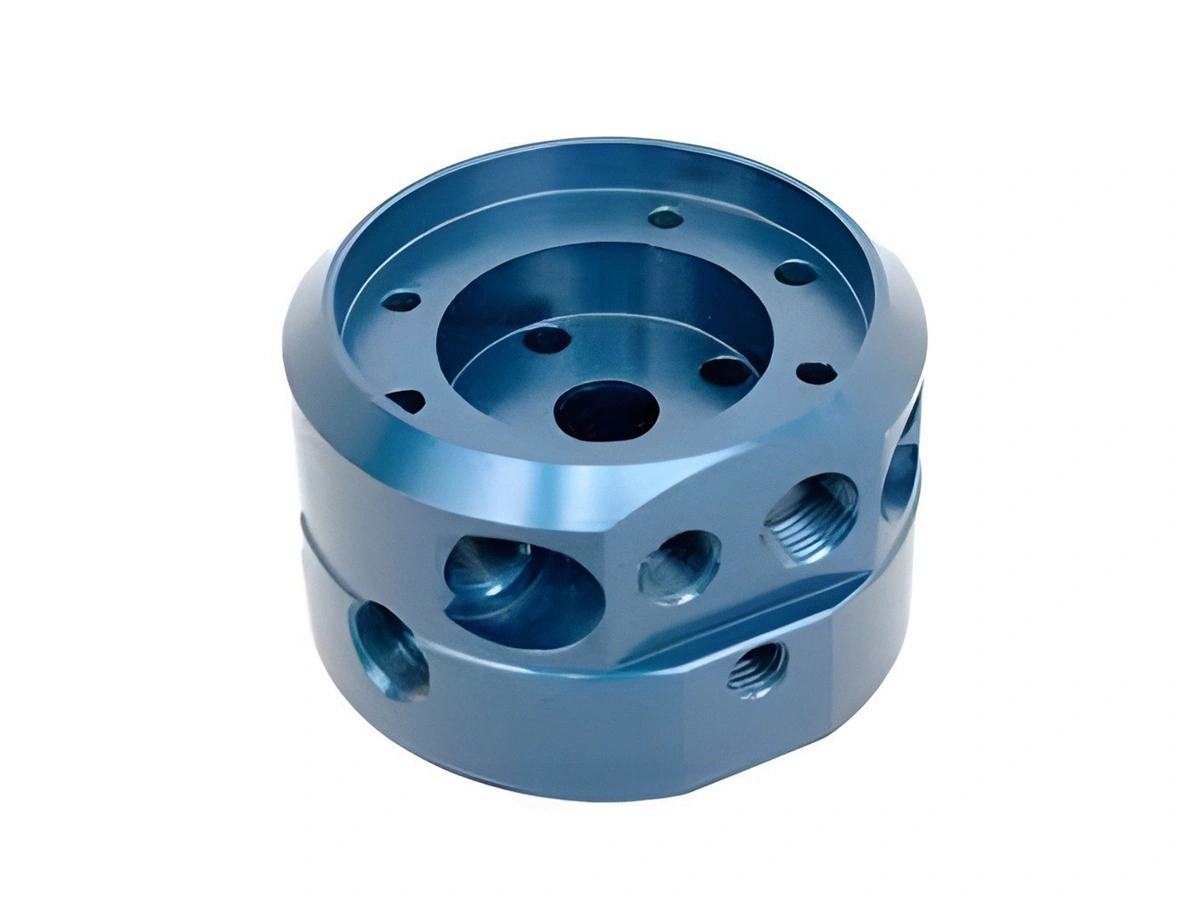
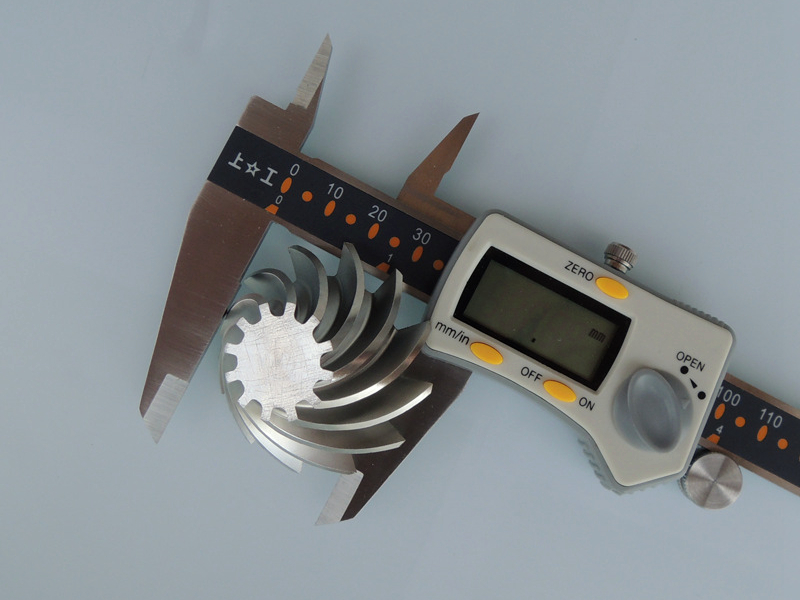
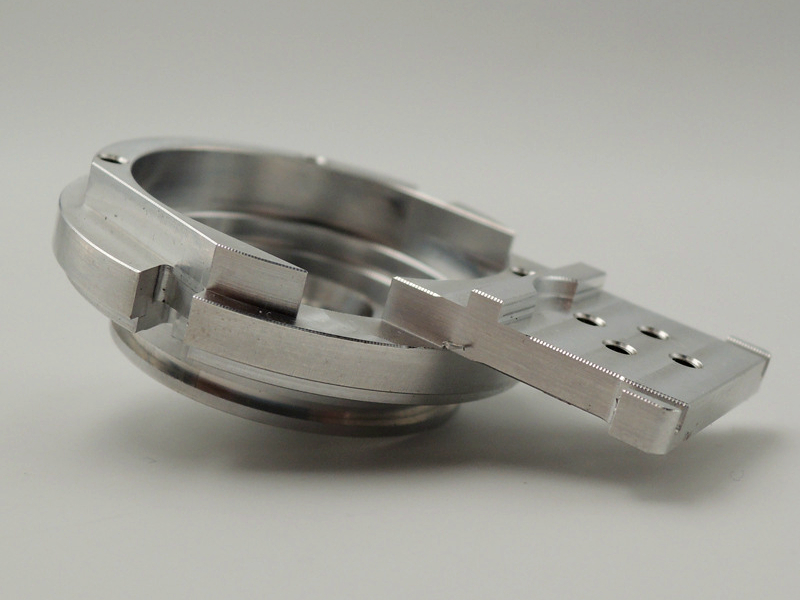
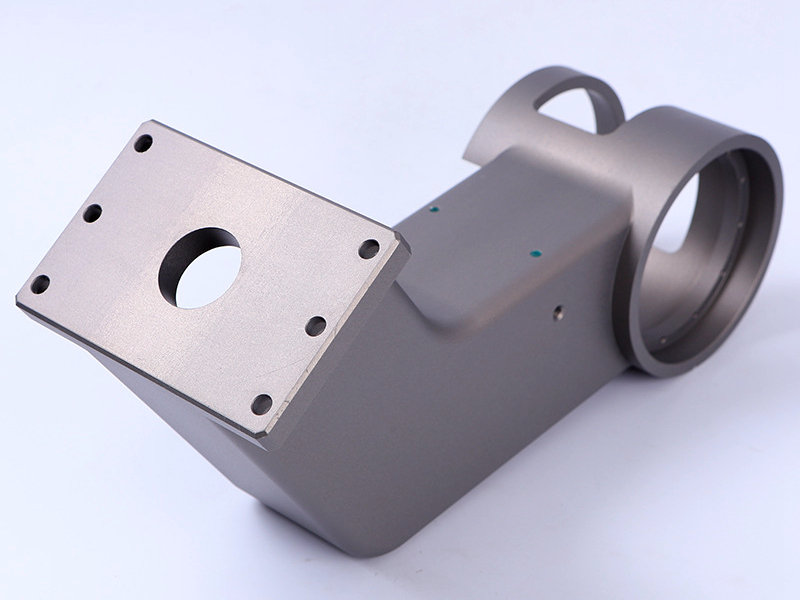
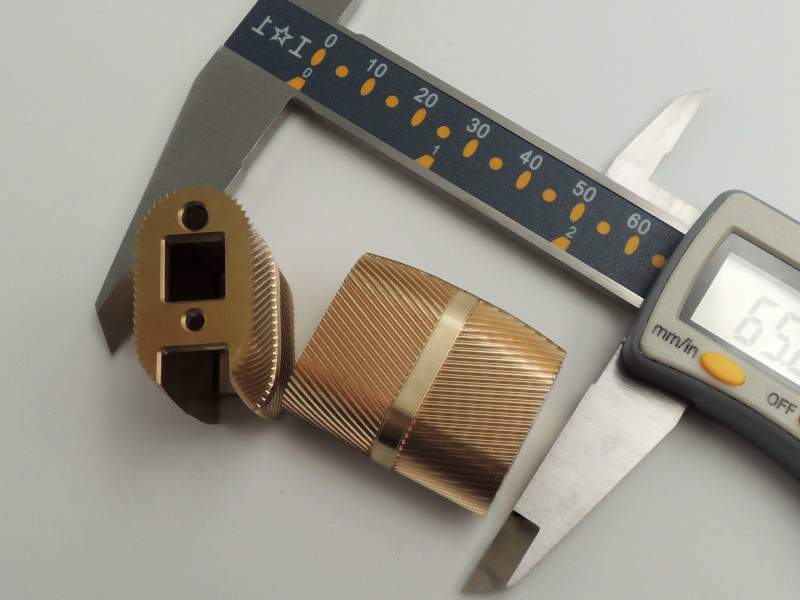
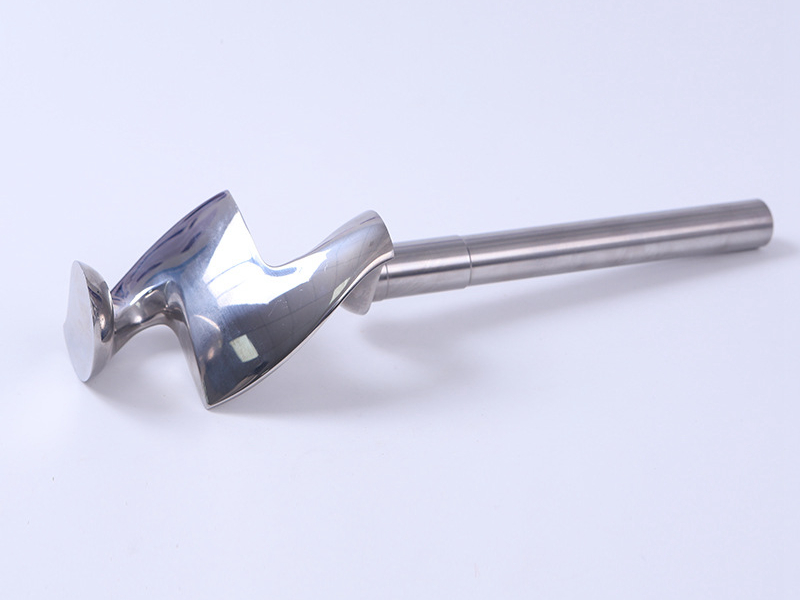
Custom Parts CNC Machining Service
Our On-Demand Precision CNC Milling Service is tailored to meet the most exacting standards for industries requiring high-quality, reliable, and efficient superalloys, ceramic, stainless steel, aluminum, and titanium parts CNC milling solutions.
- Rapid CNC Machining Prototyping
- Low Volume CNC Machining Service
- CNC Machining Mass Production Service
- One Stop CNC Machining Service

Send us your designs and specifications for a free quotation
All uploaded files are secure and confidential
Custom Components CNC Machining Manufacturing
We provide milling, turning, and multi-axis CNC precision machining services. We have mature processing technologies for advanced materials, including high-temperature alloys, iron-based metals, plastics, ceramics, etc. We also provide one-stop services, such as surface treatment, with our audited partners.
CNC Machining Materials
We can process high-temperature alloys such as Inconel, titanium alloy, etc. Iron-based alloys such as stainless steel, carbon steel, etc. Plastics such as ABS, PC, POM, PEEK, etc. Ceramics such as alumina, zirconia, etc. Mainly involved in processing high-temperature alloy structural parts for aerospace, gas turbines, and precision parts in the medical industry.
Applications of CNC Machined Parts
CNC machined parts are widely used across industries for their precision, durability, and versatility. These parts are crafted from superalloys, titanium, aluminum, stainless steel, and plastics, enabling their application in high-performance sectors such as aerospace, automotive, medical devices, power generation, and robotics. CNC machining allows for complex geometries, tight tolerances, and efficient production. It is ideal for manufacturing engine parts, structural elements, medical instruments, and industrial machinery with enhanced accuracy and repeatability.
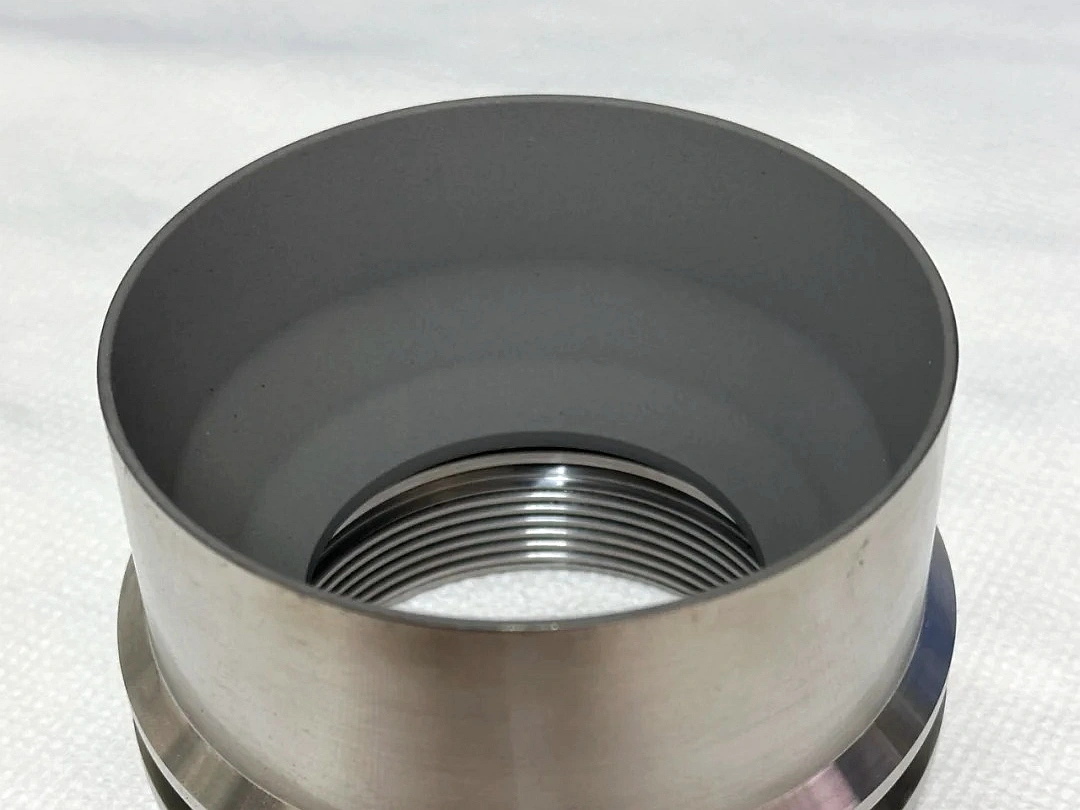
Surface Treatment for CNC Machined Parts
Surface treatment for CNC machined parts enhances durability, performance, and aesthetics by modifying the material’s surface. Standard techniques include anodizing, plating, coating, polishing, and shot peening. These treatments improve corrosion resistance, wear resistance, and surface hardness. For example, anodizing aluminum increases its resistance to corrosion, while shot peening improves fatigue resistance. Surface treatments are crucial for industries like aerospace, automotive, and medical devices, where component longevity and reliability are critical under harsh operational conditions.

Learn More
Thermal Coating

Learn More
As Machined

Learn More
Painting

Learn More
PVD (Physical Vapor Deposition)
Learn More
Sandblasting
Learn More
Electroplating

Learn More
Polishing

Learn More
Anodizing

Learn More
Powder Coating

Learn More
Electropolishing

Learn More
Passivation

Learn More
Brushing

Learn More
Black Oxide

Learn More
Heat Treatment

Learn More
Thermal Barrier Coating (TBC)

Learn More
Tumbling

Learn More
Alodine

Learn More
Chrome Plating

Learn More
Phosphating

Learn More
Nitriding

Learn More
Galvanizing

Learn More
UV Coating

Learn More
Lacquer Coating

Learn More
Teflon Coating
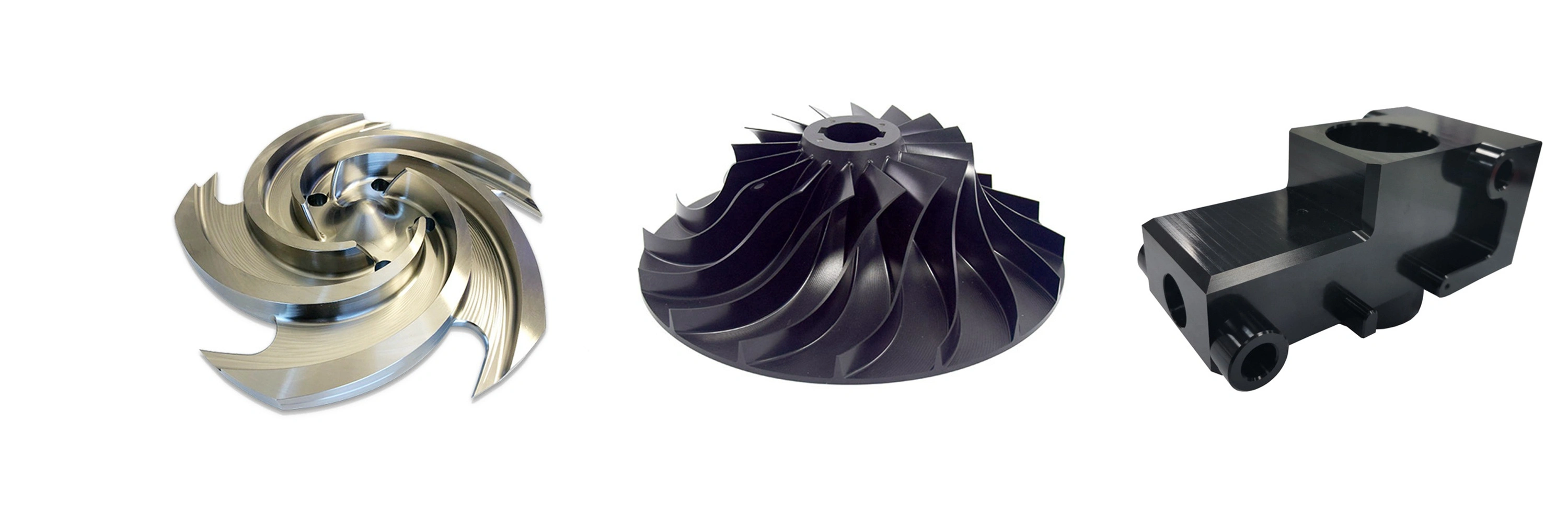
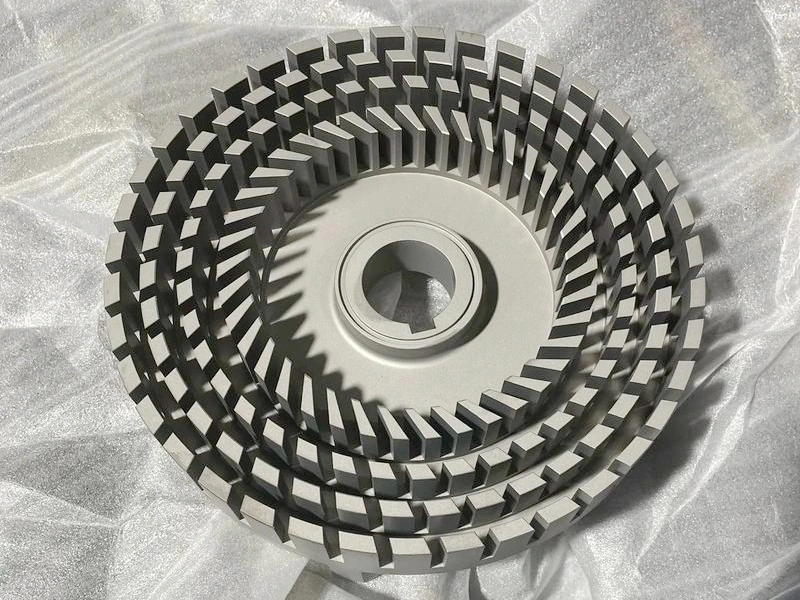
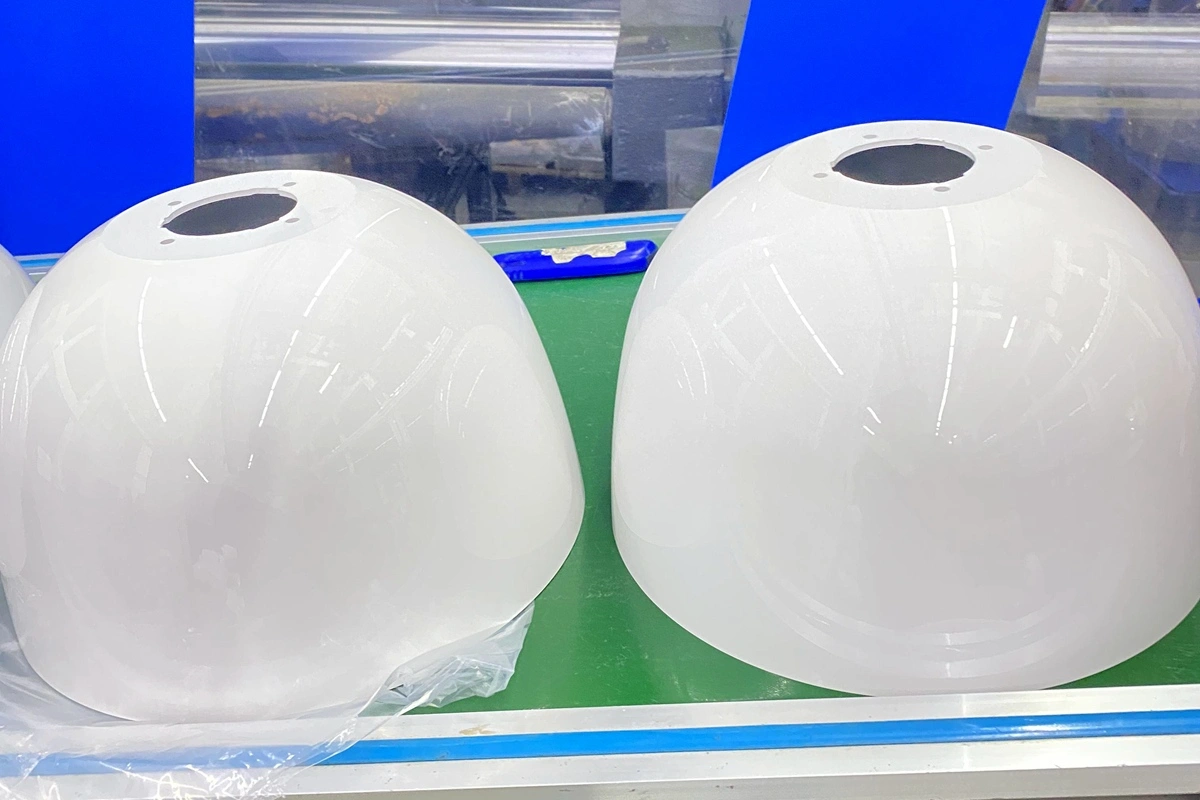
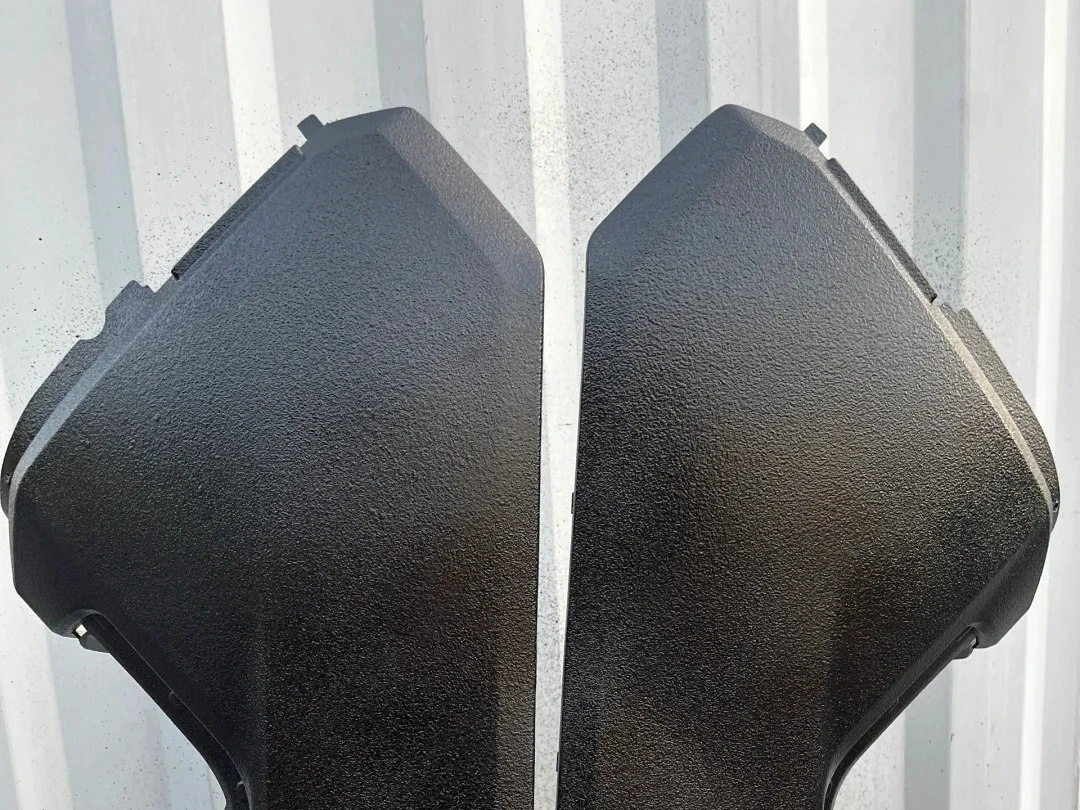
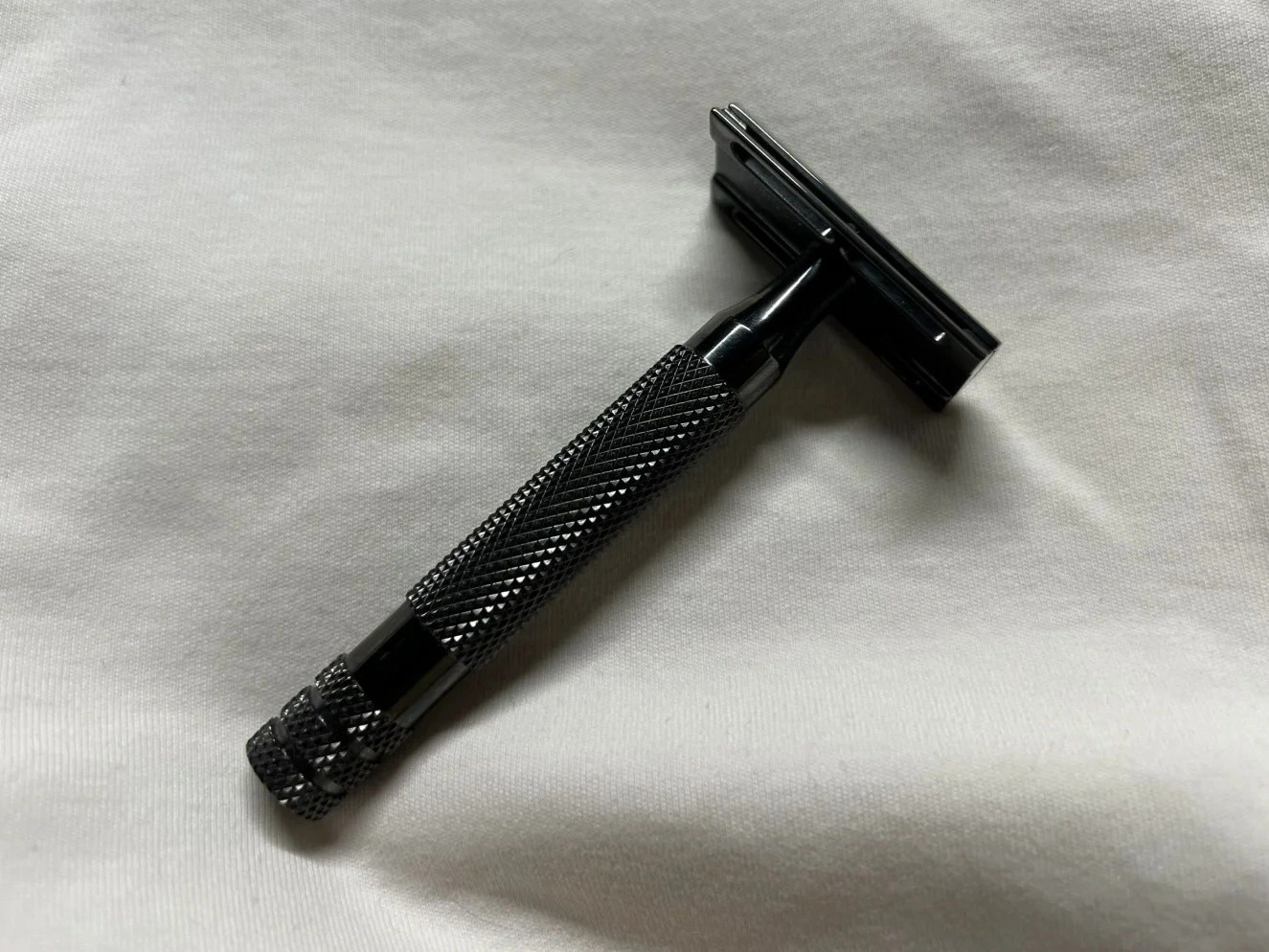
CNC Machining Components Case Study
Explore our CNC machining components case studies, showcasing precision manufacturing for industries like aerospace, automotive, medical, and more. Discover how we deliver high-quality, custom CNC machined parts using materials such as Inconel, Titanium, Aluminum, and more.
Let's Start A New Project Today
CNC Machining Tolerance
CNC machining tolerance refers to the allowable variation in part dimensions during the machining process. Tight tolerances ensure high precision, which is crucial for components requiring exact fit and function, especially in aerospace, automotive, and medical devices.
CNC Machining Design Suggestions
CNC machining design suggestions focus on optimizing parts for efficient production. Key points include using rounded corners, maintaining reasonable hole depth-to-diameter ratios, minimizing tight tolerances, ensuring tool access, simplifying shapes, and considering part weight and size. These strategies reduce machining time, cost, and complexity.
Frequently Asked Questions
Explore Related Blogs
Explore Related Resources
Solutions
Copyright © 2026 Machining Precision Works Ltd.All Rights Reserved.