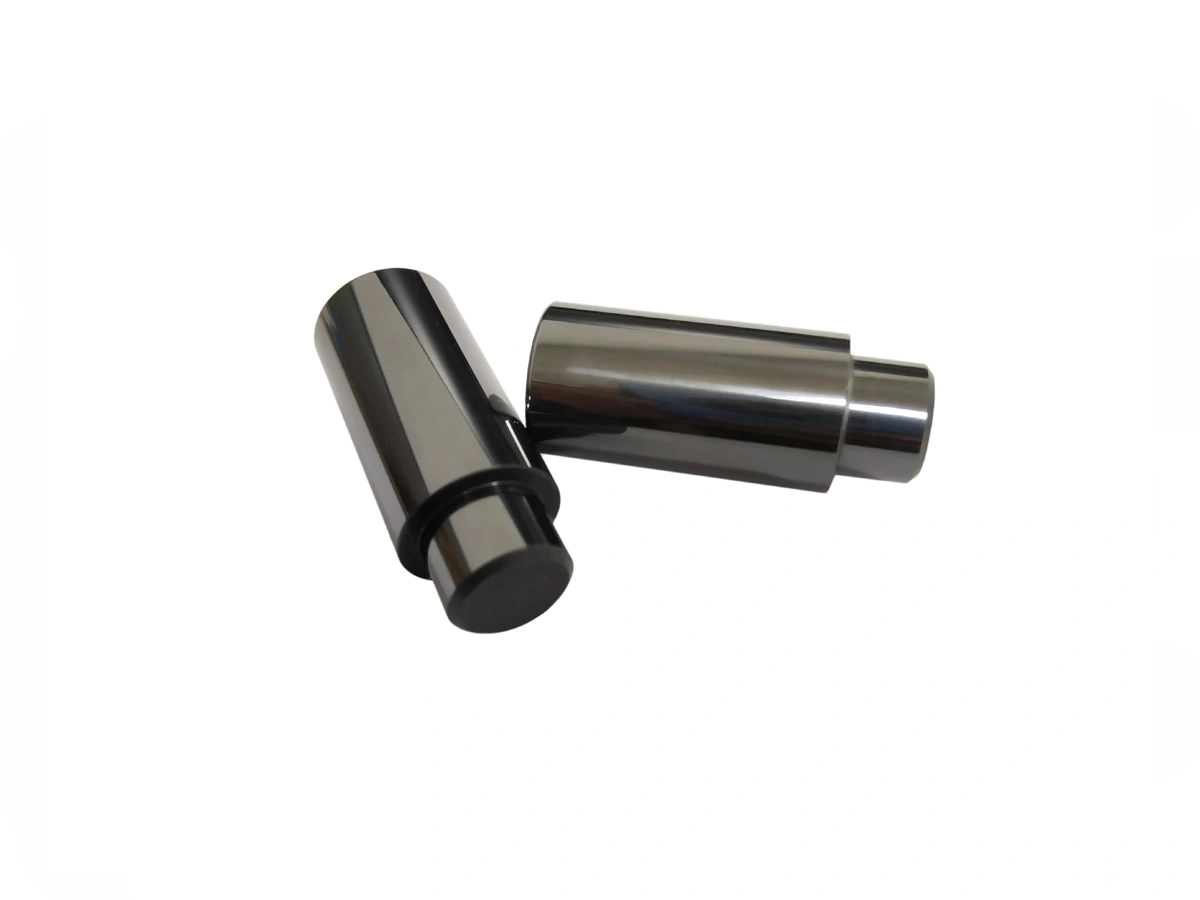
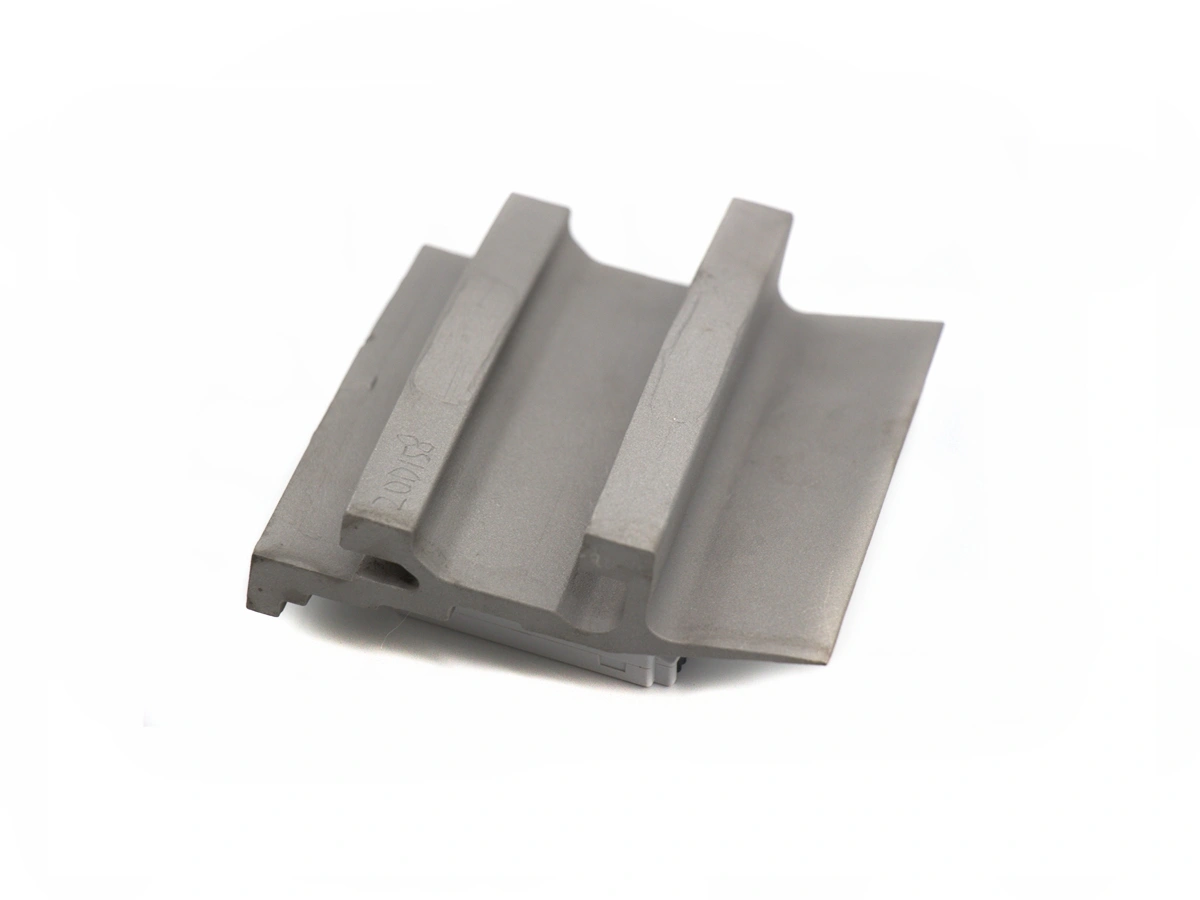
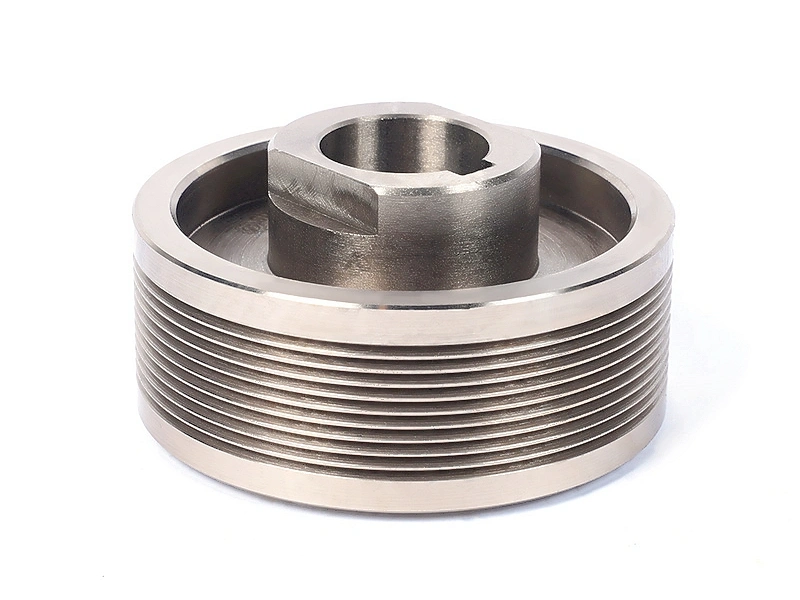
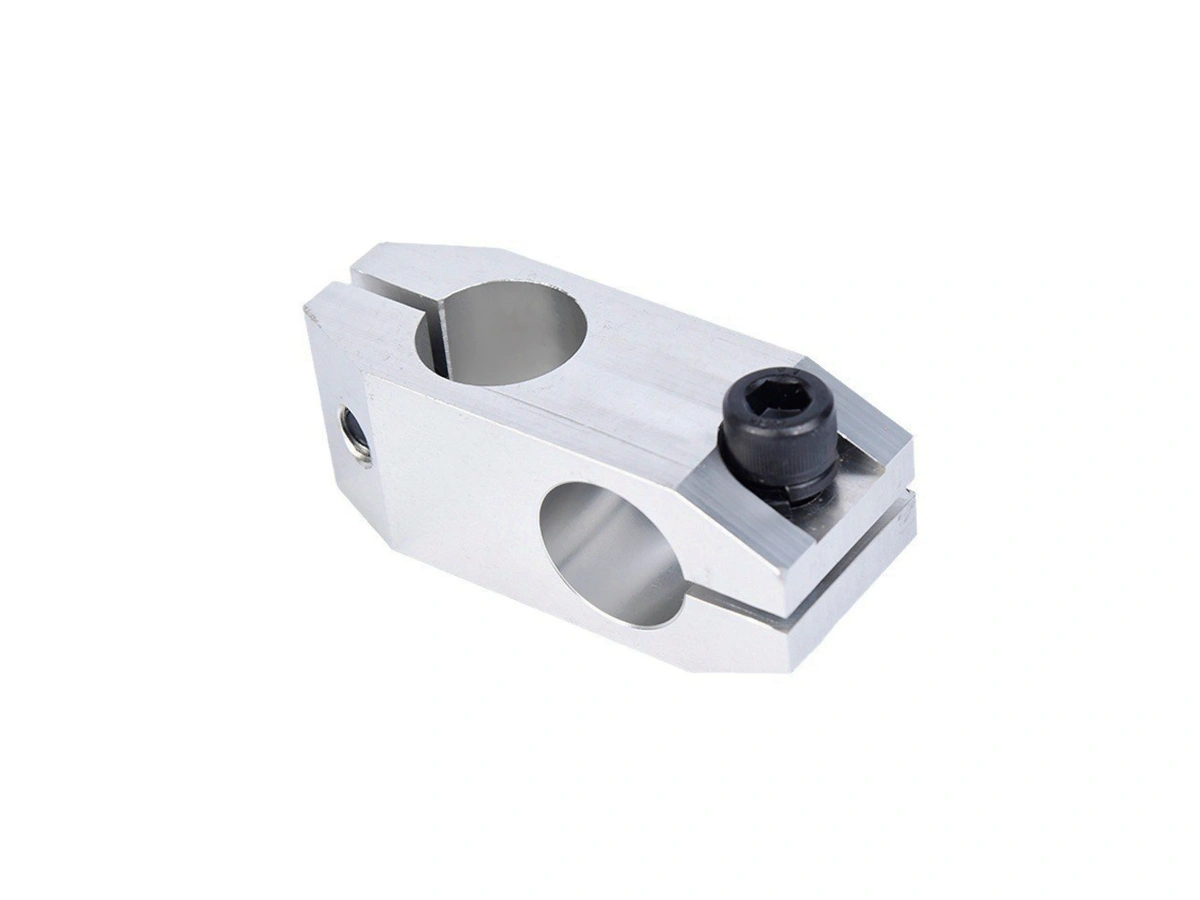
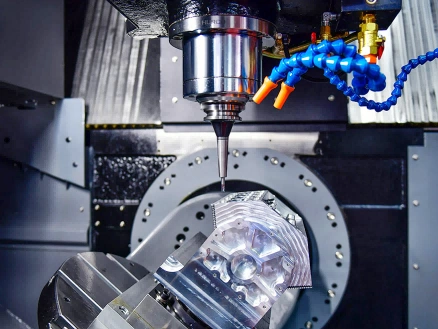
Custom Parts Manufacturing Solutions
Oil and Gas Parts Manufacturing Service
Neway provides expert Oil and Gas Parts Manufacturing services, including CNC Machining, 3D Printing, Vacuum Casting, and Investment Casting. We specialize in high-performance components for drilling, refining, and extraction applications, delivering superior precision, durability, and reliability. Our advanced manufacturing processes meet the rigorous standards of the oil and gas industry.

Custom Oil and Gas Parts Machining
Our custom oil and gas parts machining services utilize advanced CNC technologies, including milling, turning, drilling, boring, grinding, and EDM, to produce high-precision components for the industry. We specialize in manufacturing durable, high-quality parts that meet stringent performance standards, ensuring reliability in demanding environments. Multi-axis machining capabilities allow for intricate designs and tight tolerances.
Oil and Gas Material Selection
For oil and gas applications, high-performance materials such as superalloys, titanium, aluminum, copper, brass, bronze, carbon steel, stainless steel, plastic, and ceramic are crucial for manufacturing durable, corrosion-resistant, and heat-resistant components used in drilling, valves, pipelines, and offshore equipment.
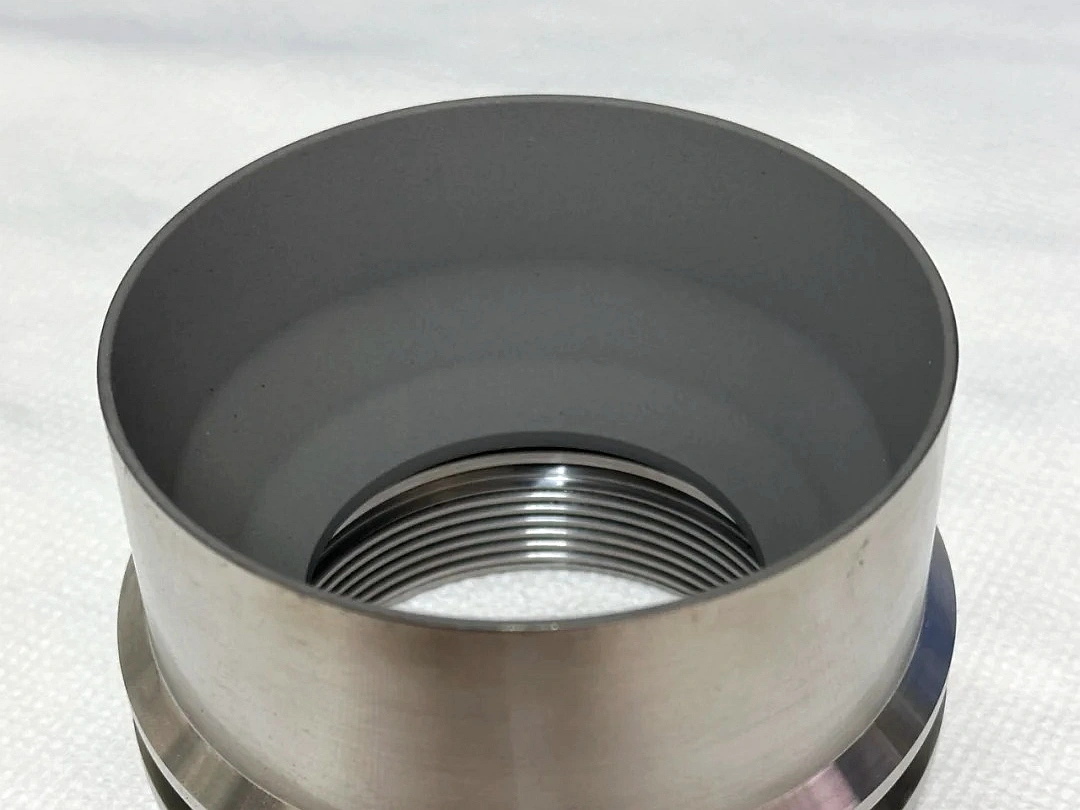
Surface Treatment for Oil and Gas Industry
Surface treatment in the oil and gas industry enhances durability and resistance of components exposed to harsh environments. Techniques like thermal coating, PVD, electroplating, anodizing, and heat treatment improve corrosion resistance, wear protection, and heat tolerance. These processes extend the lifespan of parts, ensuring reliability and safety in high-pressure, high-temperature, and chemically aggressive conditions.

Learn More
Thermal Coating
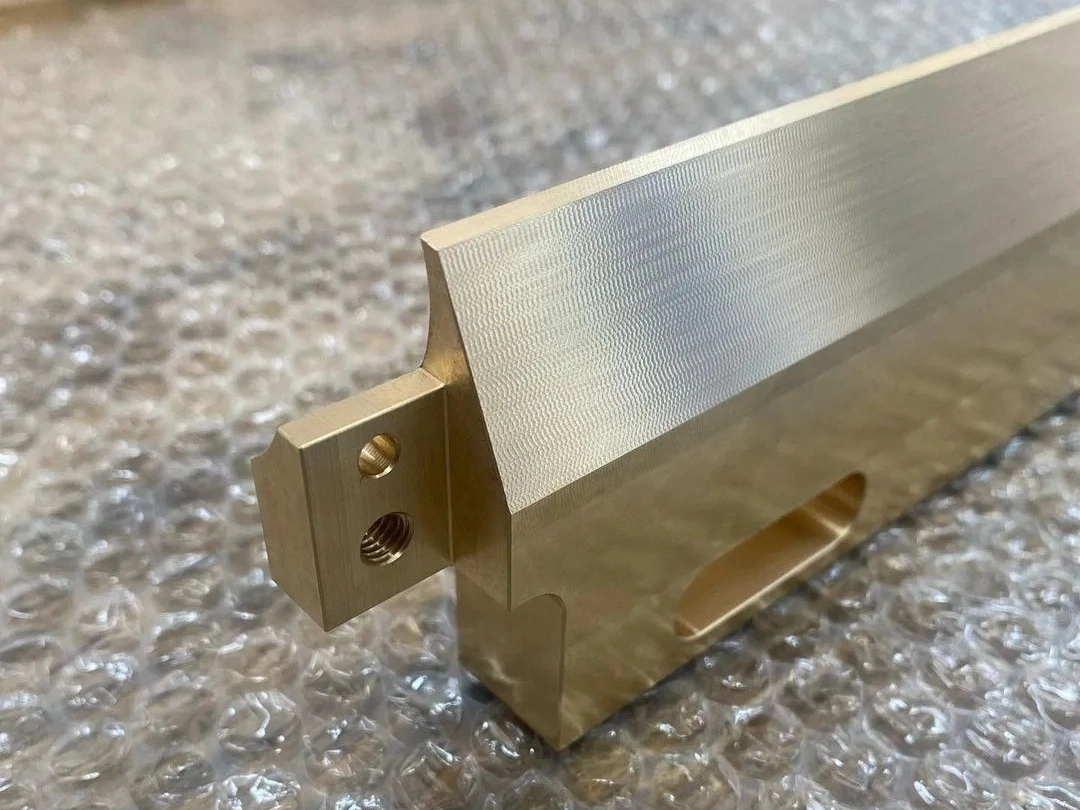

Learn More
As Machined
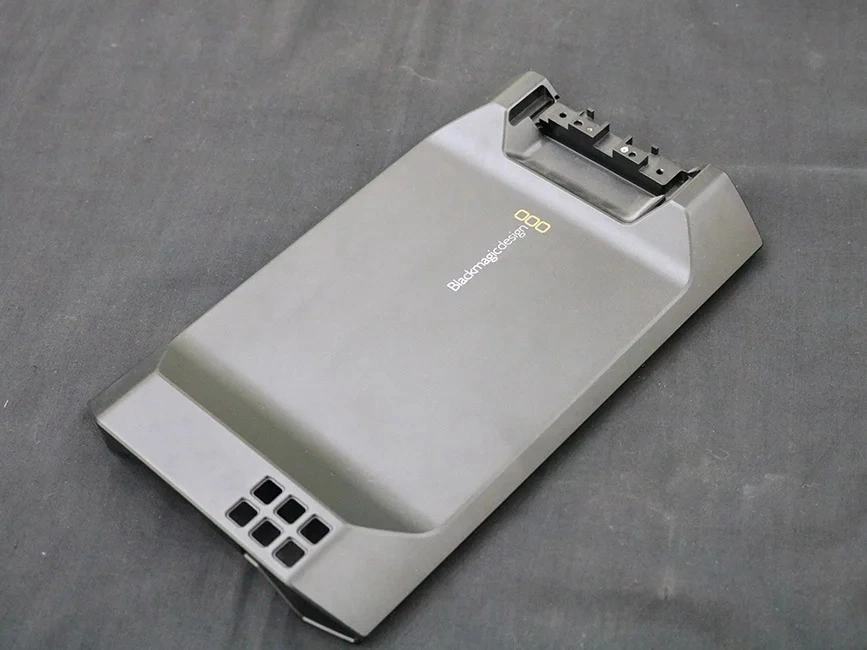

Learn More
Painting
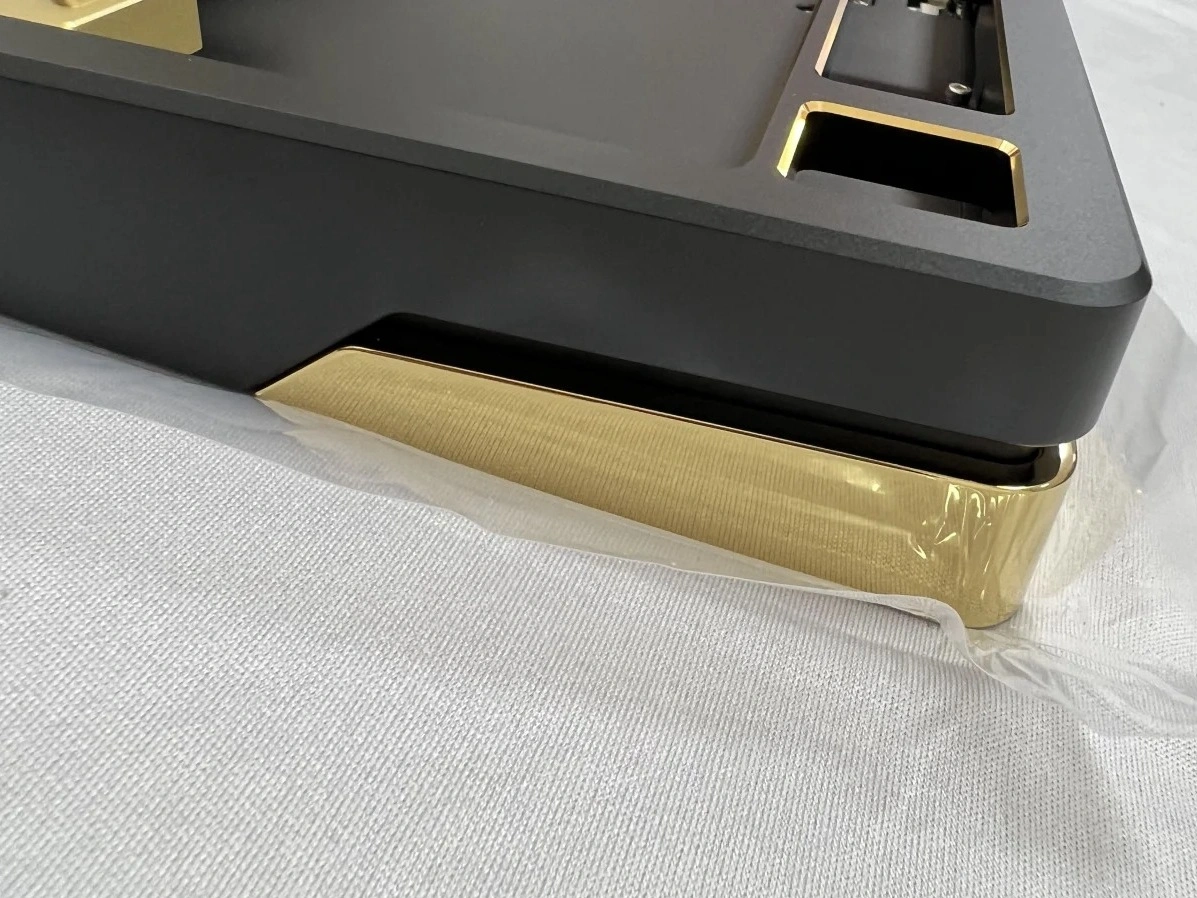

Learn More
PVD (Physical Vapor Deposition)
Learn More
Sandblasting
Learn More
Electroplating
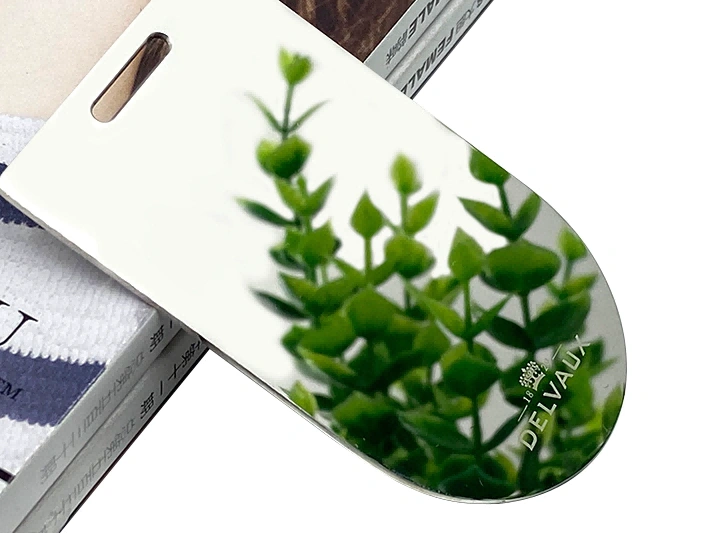

Learn More
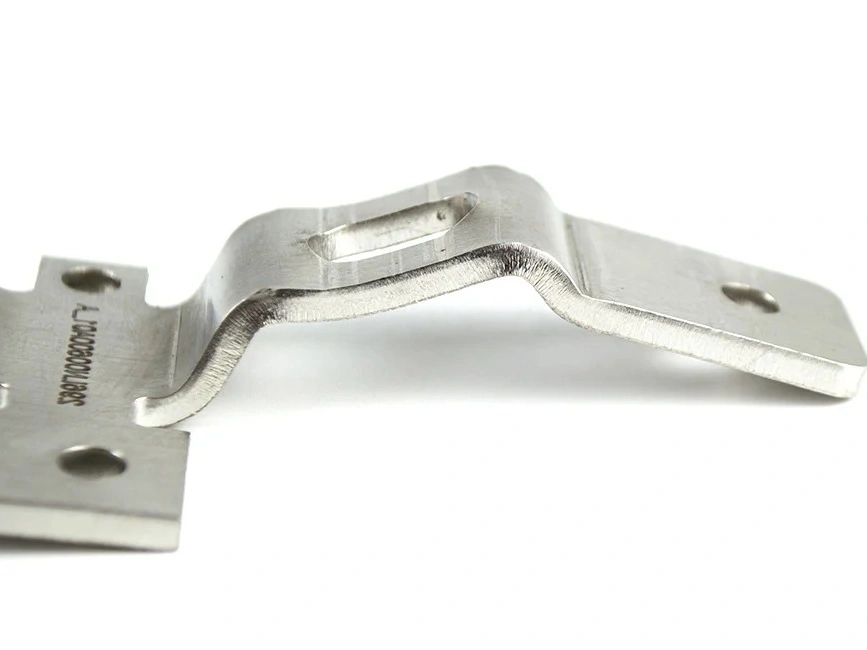
Polishing

Learn More
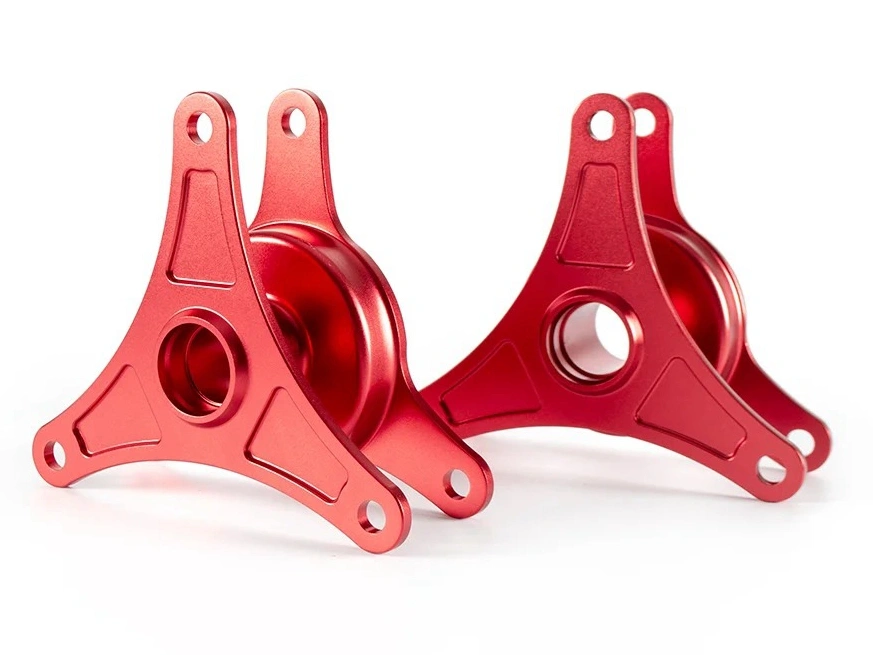
Anodizing

Learn More
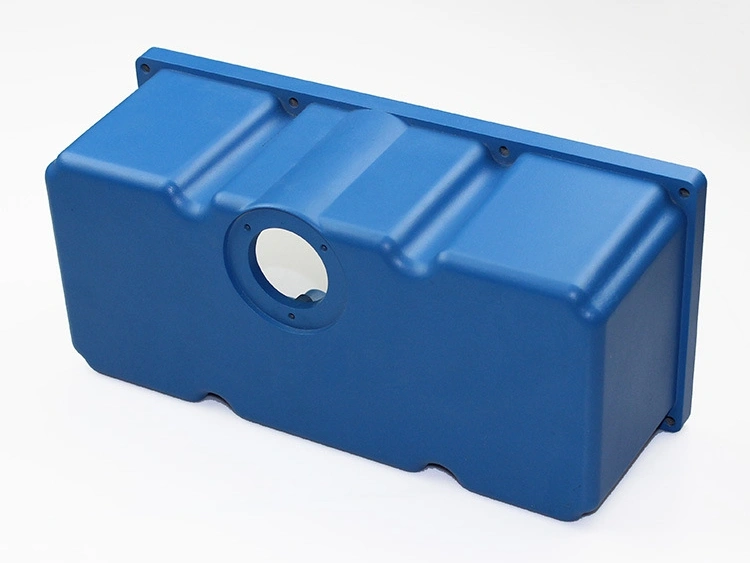
Powder Coating

Learn More
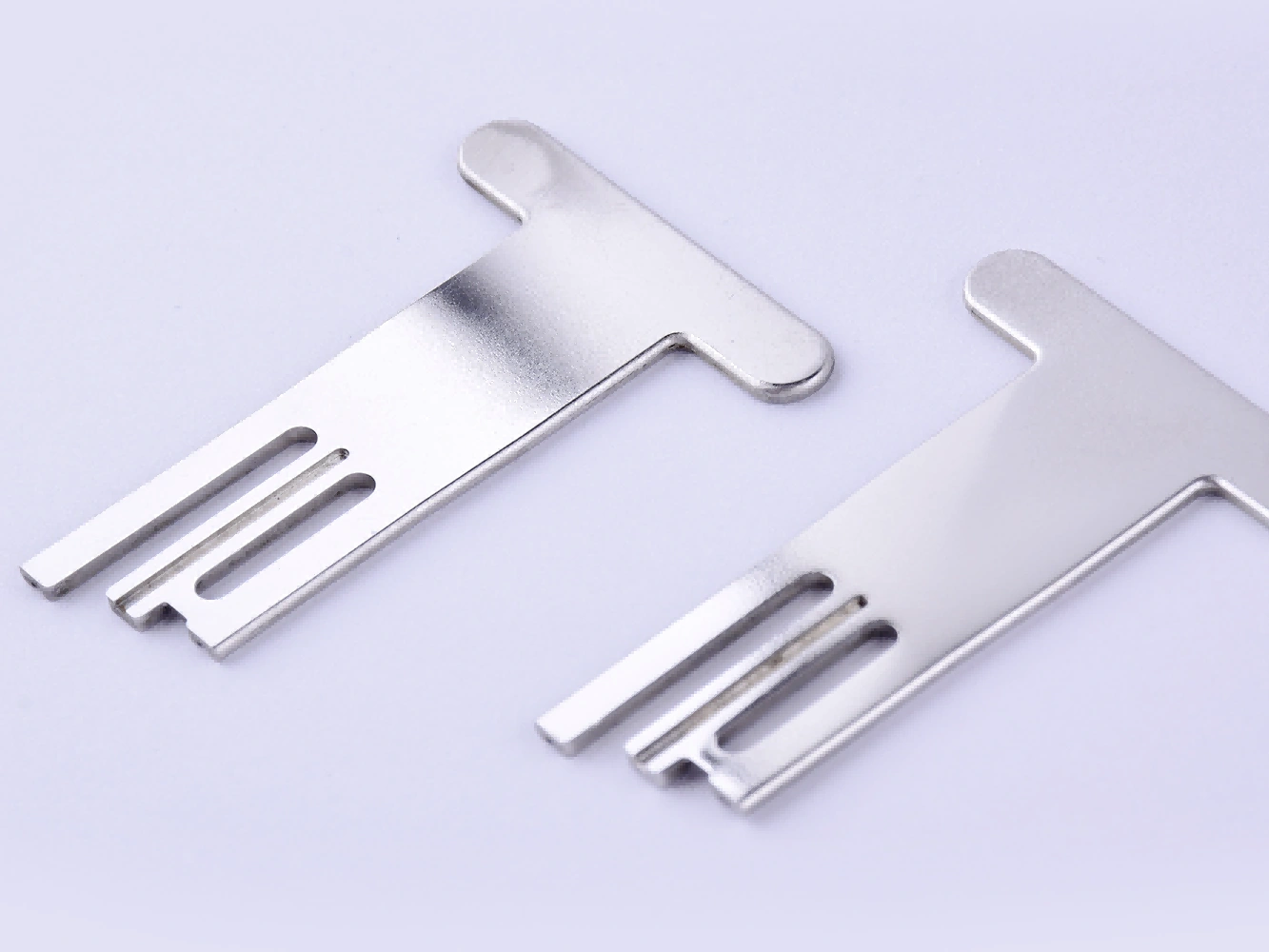
Electropolishing

Learn More
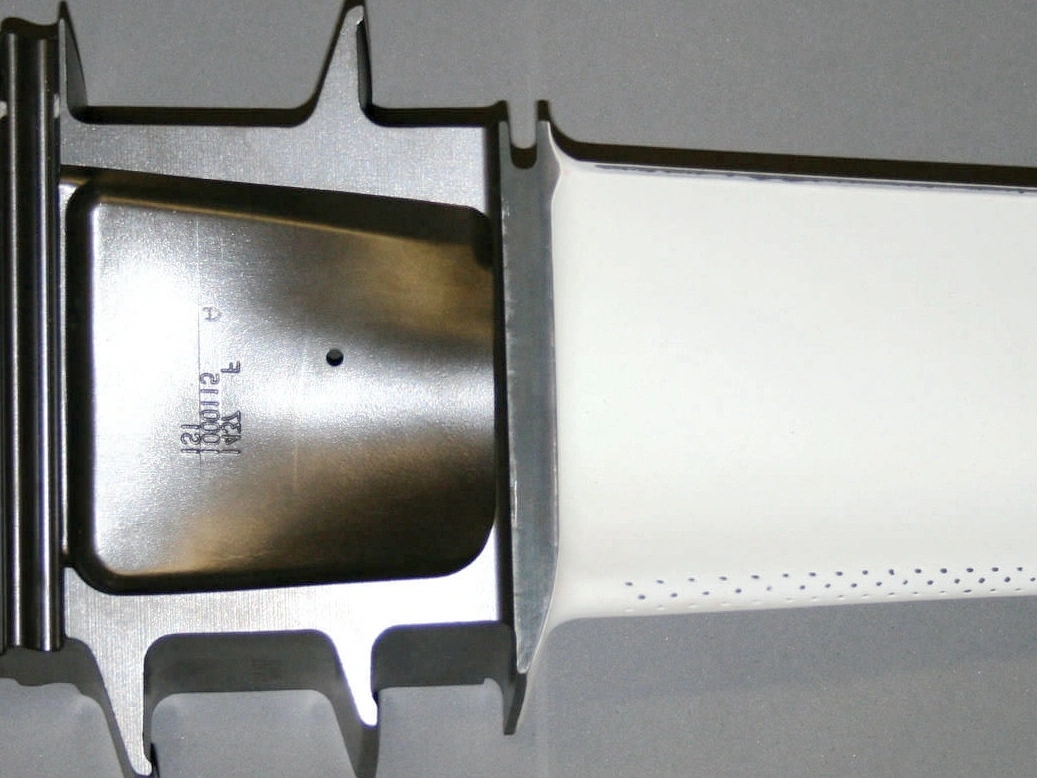
Passivation

Learn More
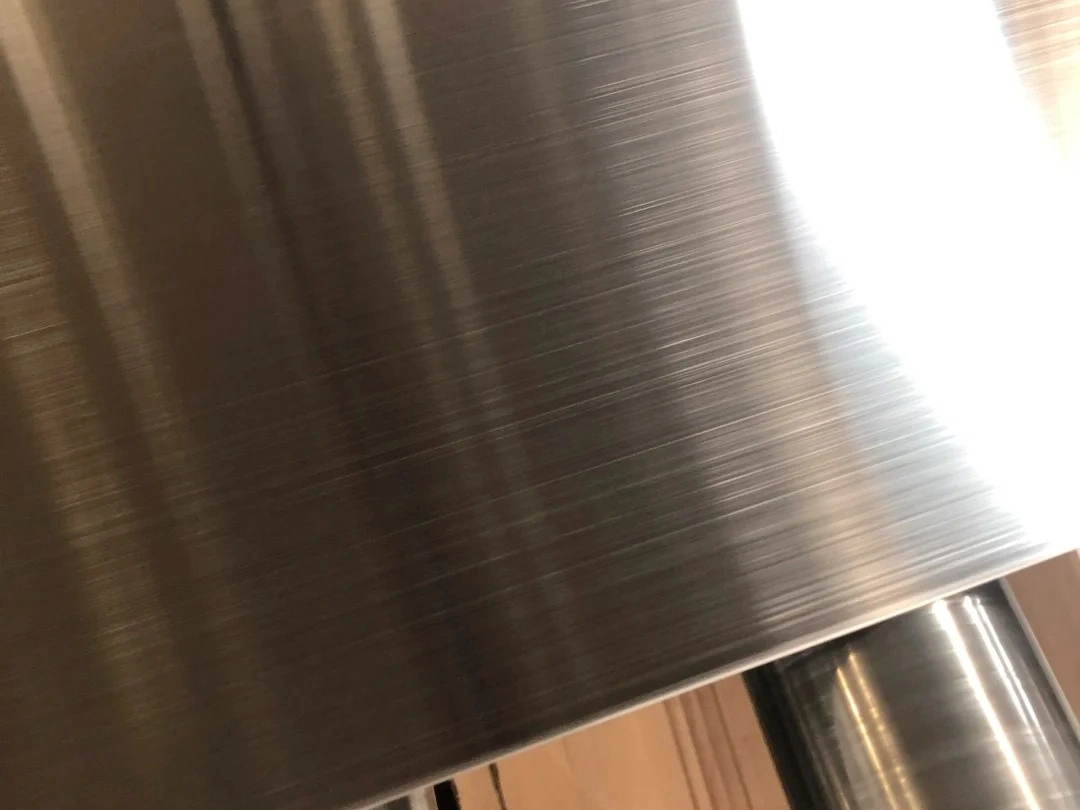
Brushing

Learn More
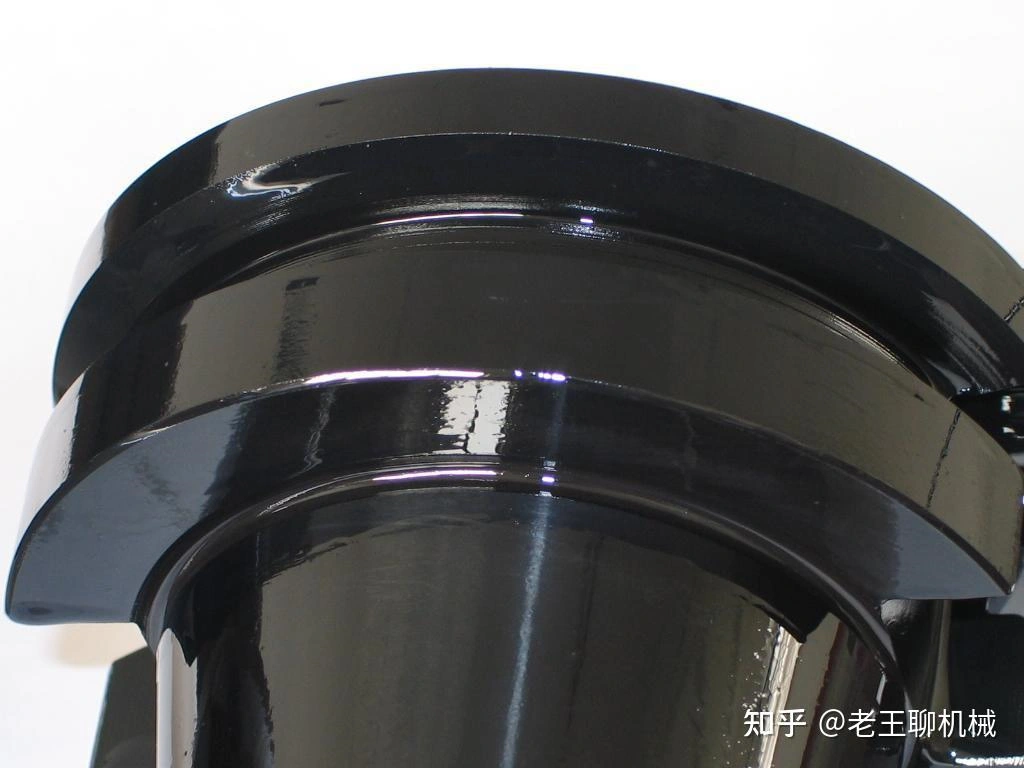
Black Oxide

Learn More
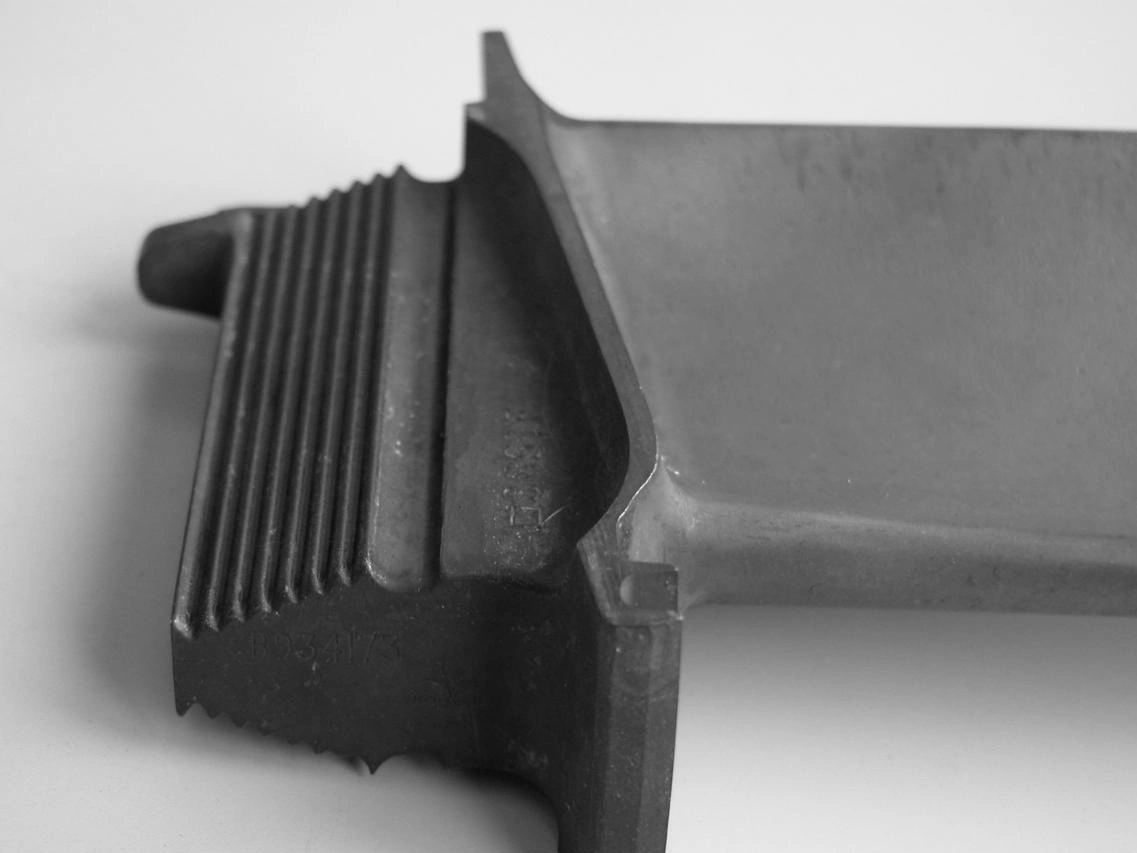
Heat Treatment

Learn More
Thermal Barrier Coating (TBC)

Learn More
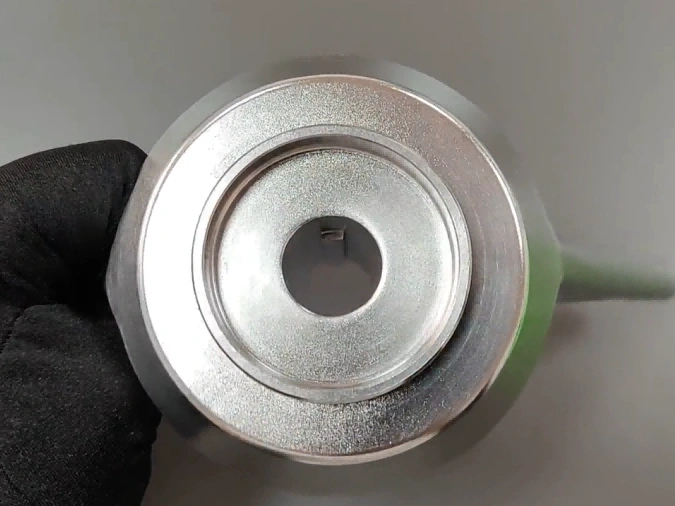
Tumbling

Learn More
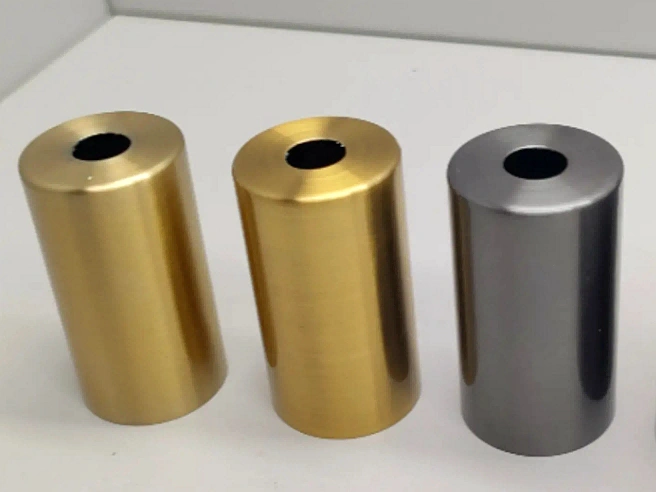
Alodine

Learn More
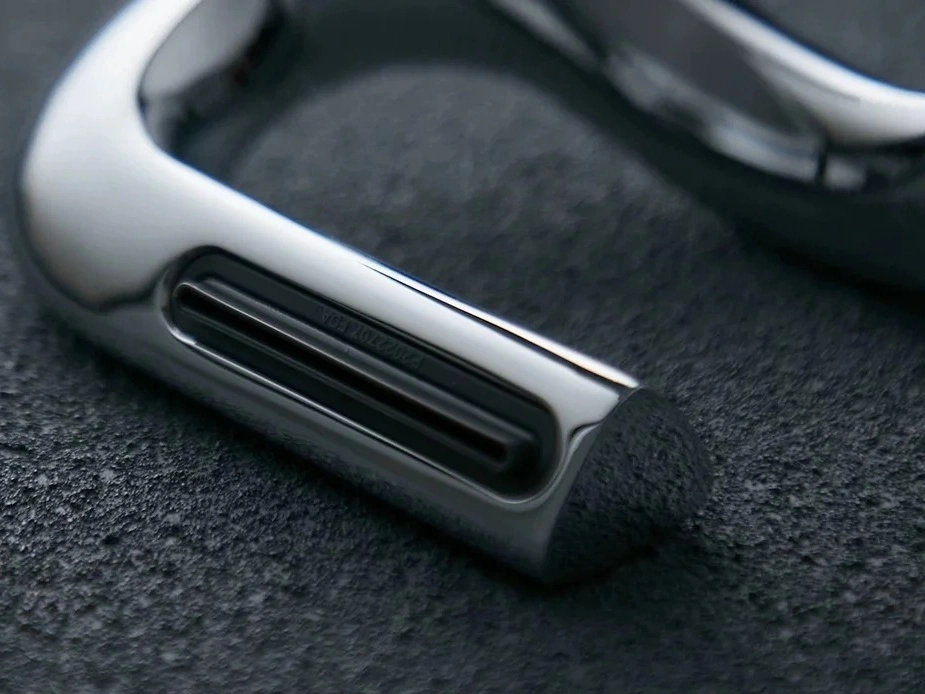
Chrome Plating

Learn More
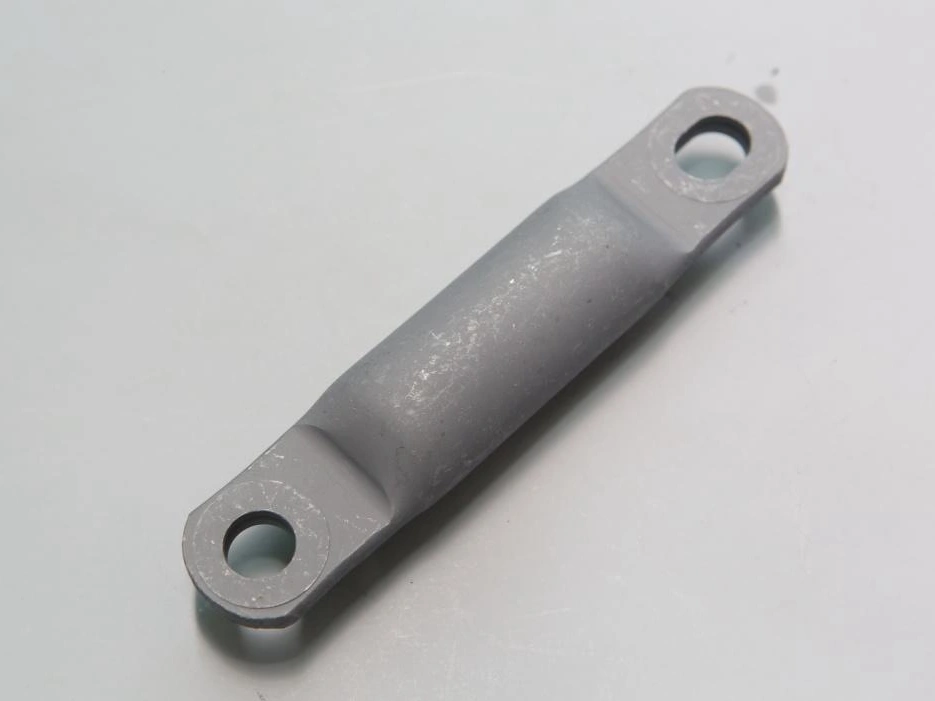
Phosphating

Learn More
Nitriding

Learn More
Galvanizing

Learn More
UV Coating

Learn More
Lacquer Coating

Learn More
Teflon Coating
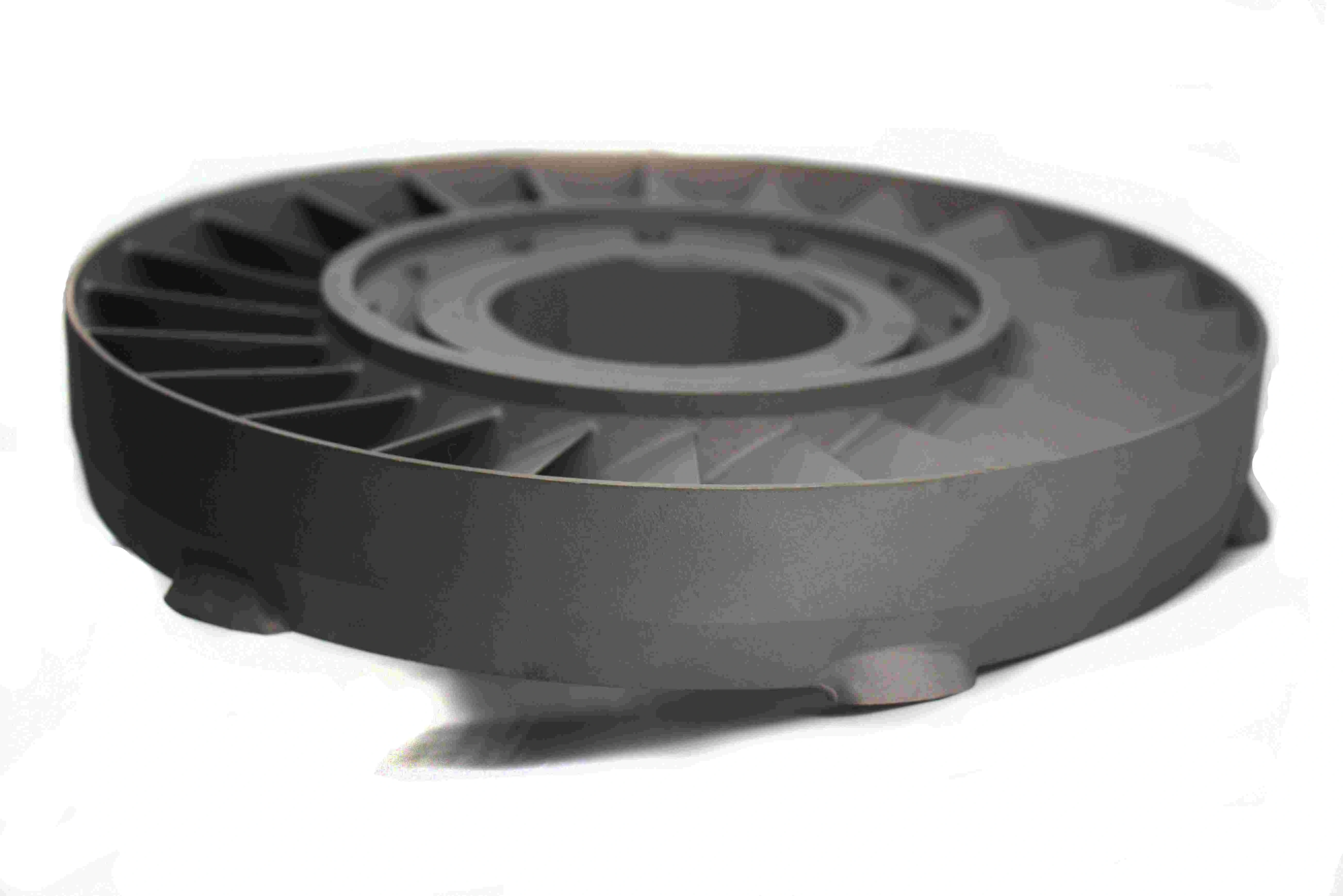
CNC Machining for Oil and Gas Equipment
CNC machining is used to create robust parts for the oil and gas industry, including valves, pipes, and drill bits, ensuring precision and resilience under extreme pressure and harsh conditions.
Let's Start A New Project Today
Guide to Oil and Gas Parts Design
Designing parts for the oil and gas industry requires materials that can withstand extreme pressures, temperatures, and corrosive environments. This guide outlines engineering best practices for durable, reliable, and compliant oil and gas components.
Custom Oil and Gas Parts Manufacturing Considerations
Custom manufacturing of oil and gas parts requires robust materials, precise engineering, and compliance with safety and performance standards. This guide outlines essential manufacturing considerations to produce reliable, high-performance oil and gas components.
Frequently Asked Questions
Explore Related Resources
Solutions
Copyright © 2026 Machining Precision Works Ltd.All Rights Reserved.