Qual tratamento de superfície oferece melhor resistência à corrosão marinha?
Desafios Ambientais em Condições Marinhas
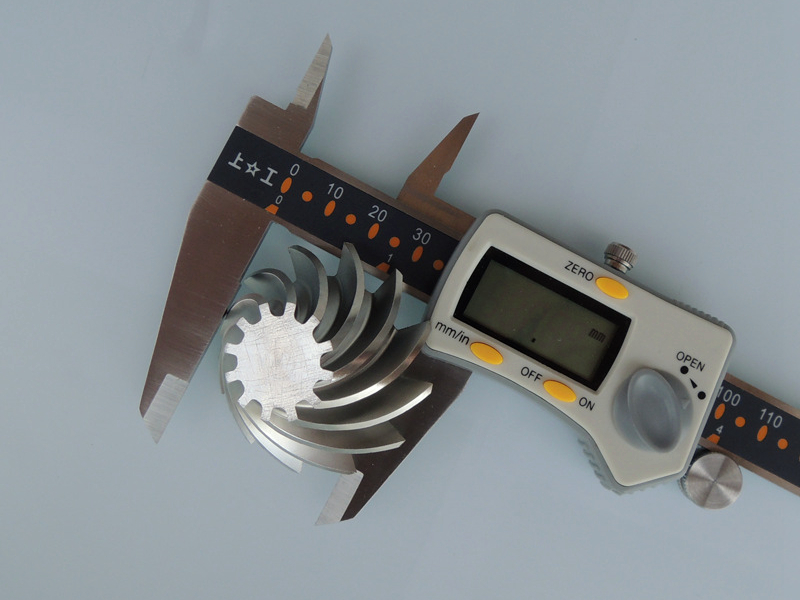
Ambientes marinhos expõem componentes CNC à exposição contínua à água salgada, alta umidade e interações galvânicas. Esses fatores aceleram a oxidação e a corrosão por pite, tornando essencial o uso de usinagem CNC e acabamentos resistentes à corrosão. Materiais como aço inoxidável 316L, bronze de alumínio C63000 e titânio Ti-6Al-4V já oferecem resistência intrínseca, mas tratamentos superficiais protetores estendem ainda mais a vida útil dos componentes.
Principais Tratamentos de Superfície para Proteção Contra Corrosão
Para ligas de alumínio, a anodização cria uma camada de óxido dura e não condutiva que melhora significativamente a resistência em ambientes marinhos. As anodizações Tipo II e Tipo III são comumente aplicadas em peças de Alumínio 6061-T6 ou Alumínio 7075 utilizadas em estruturas e carcaças marítimas. Para ligas ferrosas, o revestimento de óxido negro oferece proteção moderada; no entanto, uma opção mais durável é a galvanização, que forma uma camada de barreira de zinco para evitar a formação de ferrugem. Quando combinada com cromagem, a resistência à corrosão aumenta significativamente, especialmente em eixos e fixadores de aço. Para os aços inoxidáveis, a passivação remove o ferro livre e reforça a camada natural de óxido de cromo, proporcionando uma película passiva estável ideal para aplicações subaquáticas. Da mesma forma, o revestimento PVD ou o revestimento de Teflon podem oferecer resistência química adicional em ambientes agressivos com alto teor de sal.
Combinação de Materiais e Preparação de Usinagem
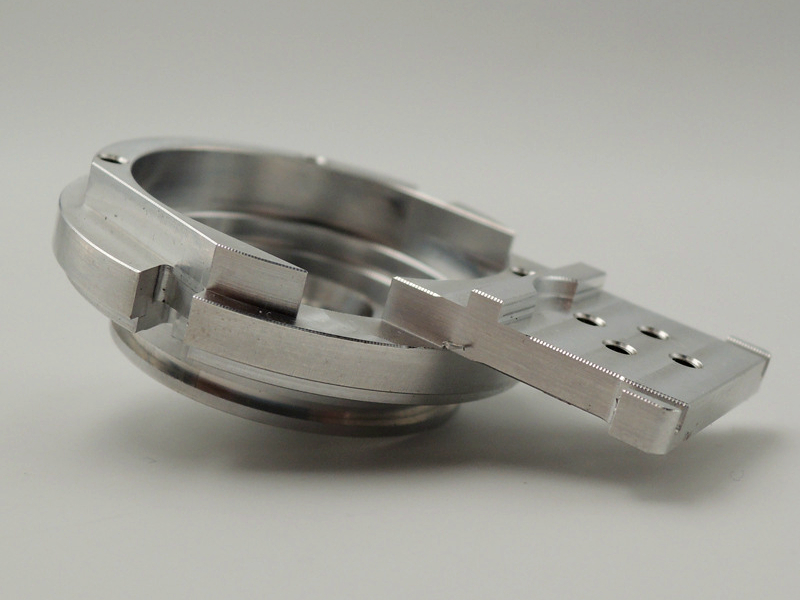
A proteção superficial eficaz começa com a seleção de materiais adequados e uma preparação meticulosa da superfície. A usinagem de precisão e o retificação CNC garantem uniformidade para melhor adesão do revestimento. Ao trabalhar com ligas marinhas de bronze ou cobre-níquel, como Cobre C706 e bronze de manganês C86300, revestimentos adicionais podem não ser necessários, pois esses materiais resistem naturalmente à corrosão em água do mar.
Aplicações Industriais e Boas Práticas
Nos setores aeroespacial e de aviação, fixadores anodizados e passivados são padrão em montagens leves expostas à umidade. A indústria de geração de energia depende de componentes galvanizados e revestidos para turbinas offshore. Em sistemas de óleo e gás, revestimentos marítimos como Teflon e PVD evitam a degradação corrosiva em ambientes de perfuração ricos em sal.
Conclusão
Para componentes CNC de alumínio e titânio, a anodização continua sendo o melhor equilíbrio entre resistência à corrosão e eficiência de peso. Os componentes de aço inoxidável alcançam a proteção máxima por meio de passivação ou revestimentos PVD, enquanto as peças de aço se beneficiam mais da galvanização ou cromagem. A escolha do tratamento correto depende do material, do ambiente e da duração do serviço — todos fatores críticos para aplicações marítimas confiáveis.