Online Rapid Molding Prototyping Service
Our Online Rapid Molding Prototyping Service offers fast and cost-effective solutions with rapid vacuum casting, plastic injection molding, metal injection molding, and ceramic injection molding. We provide high-quality prototypes for various industries, ensuring quick turnaround times and precision.
- Rapid Molding Prototyping Service
- Low Volume Molding Manufacturing Service
- Mass Molding Production Service
- One Stop Molding Service

Send us your designs and specifications for a free quotation
All uploaded files are secure and confidential
Rapid Molding Service Range
Our Rapid Molding Service Range includes rapid vacuum casting, plastic injection molding, metal injection molding, and ceramic injection molding. We deliver quick, accurate prototypes and production parts, ensuring high-quality results for a wide range of industries and applications.
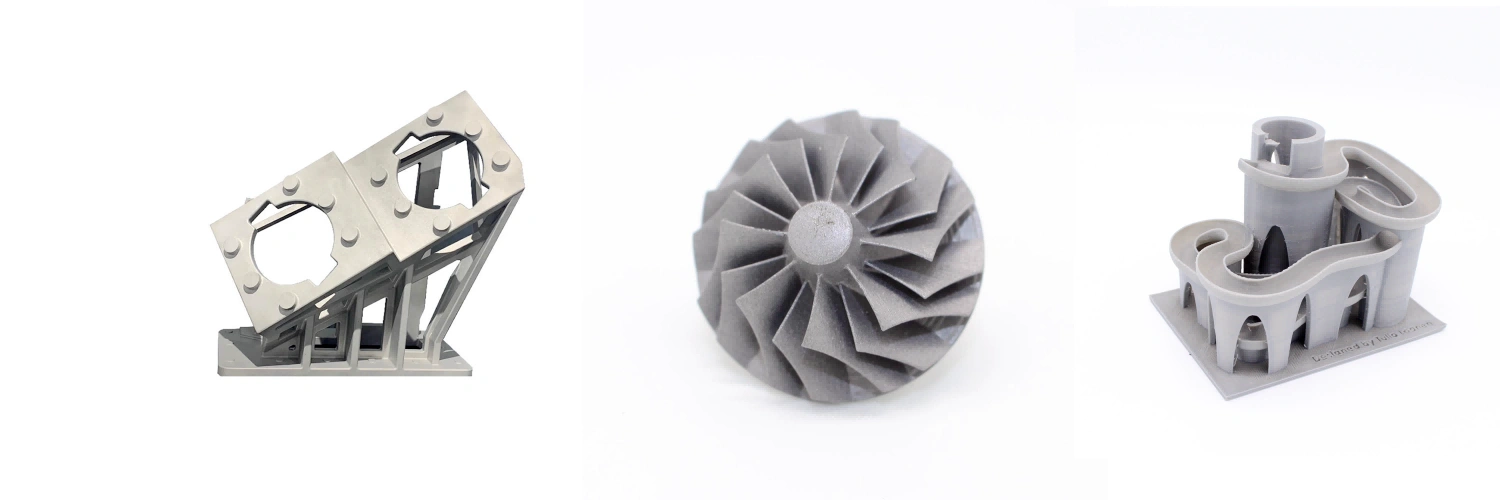
Typical 3D Printing Materials
Common aluminum alloys used in CNC machining include 6061, 7075, 2024, and 5052, offering a range of properties like high strength, corrosion resistance, and machinability. These alloys are used in aerospace, automotive, marine, and structural applications.
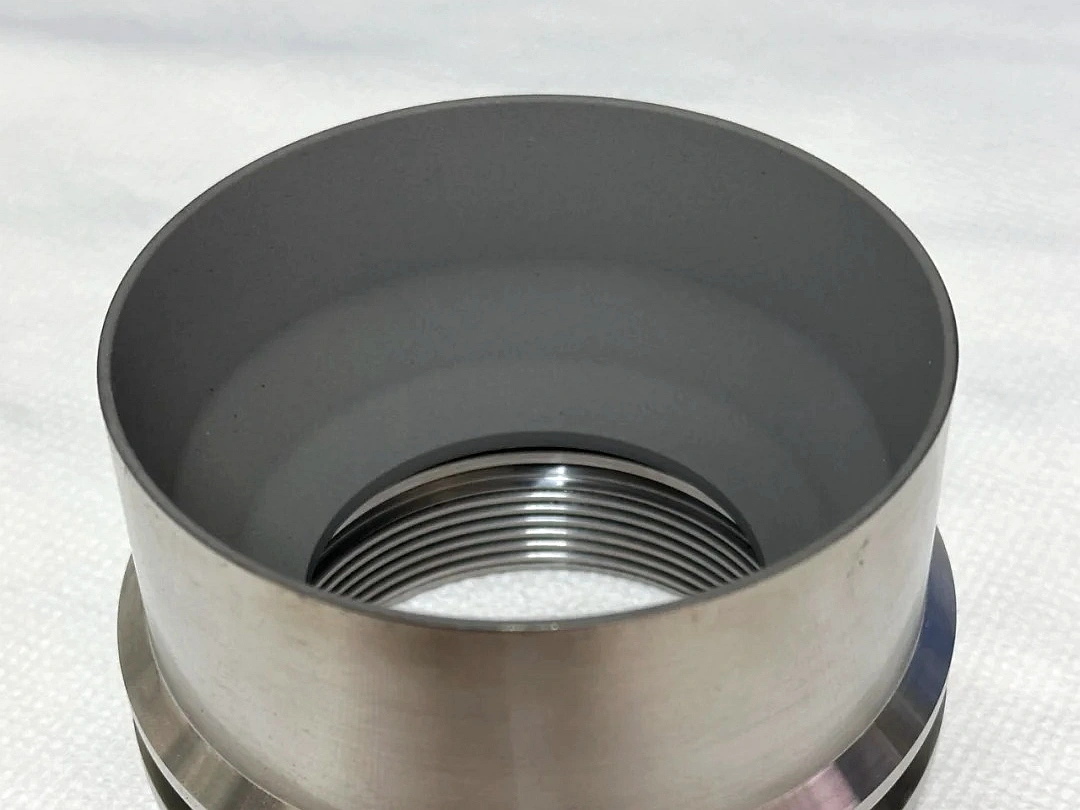
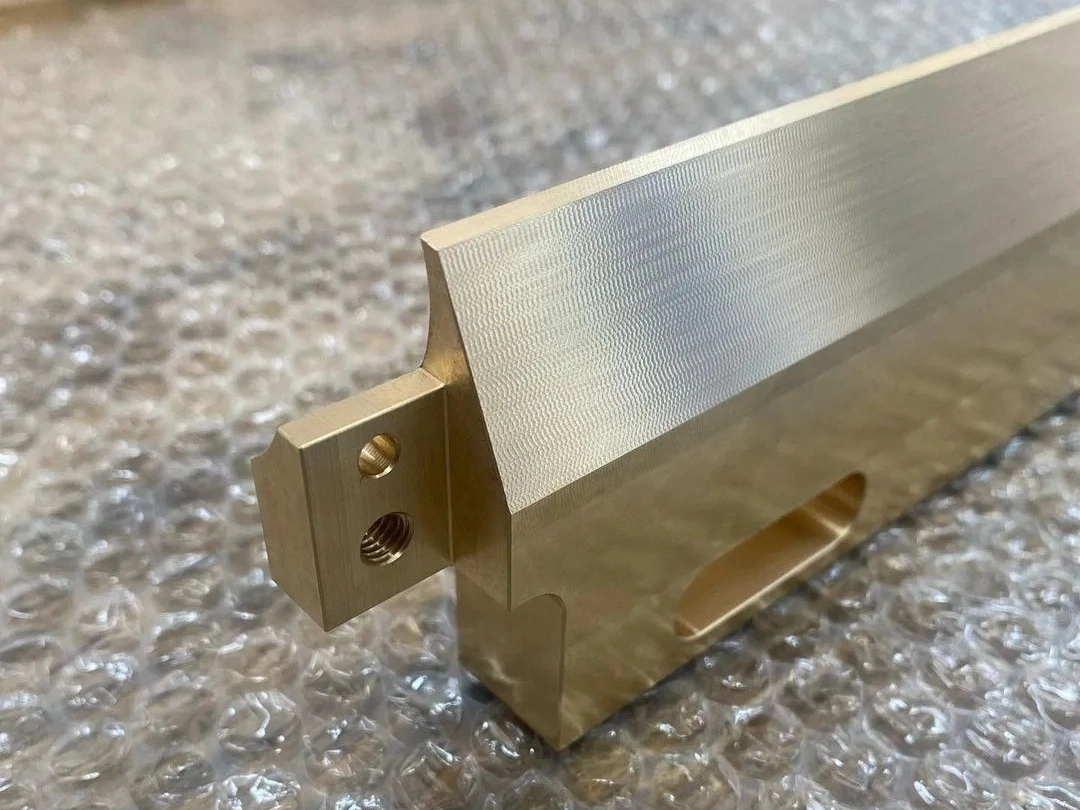
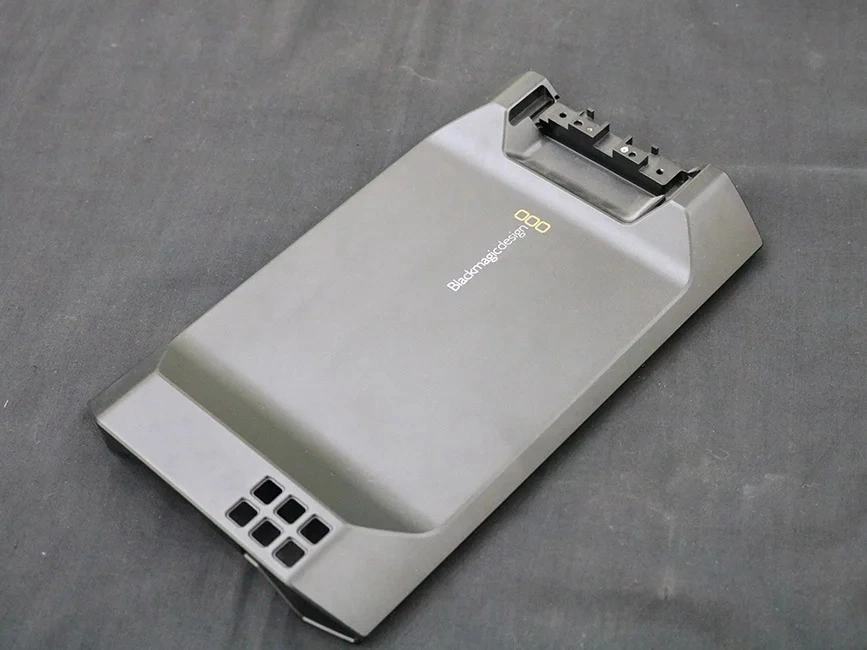
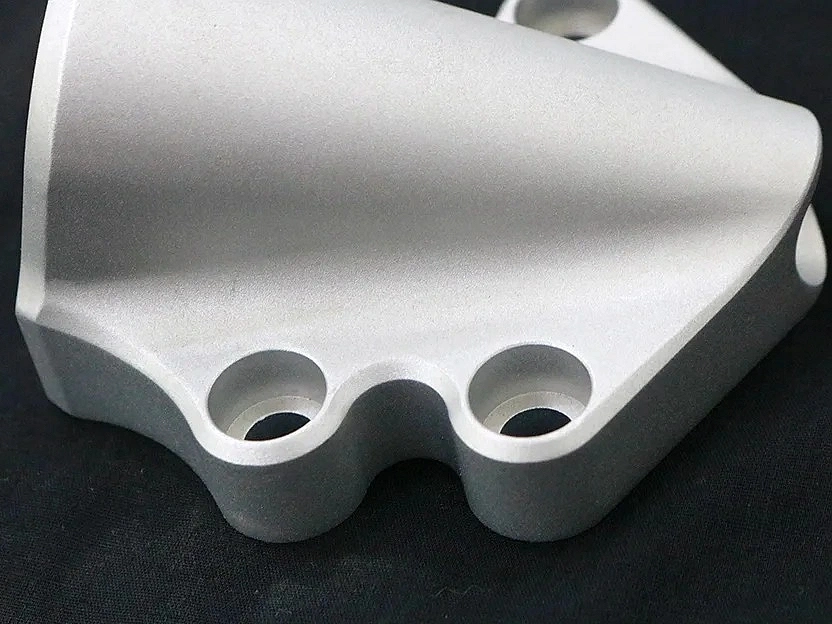
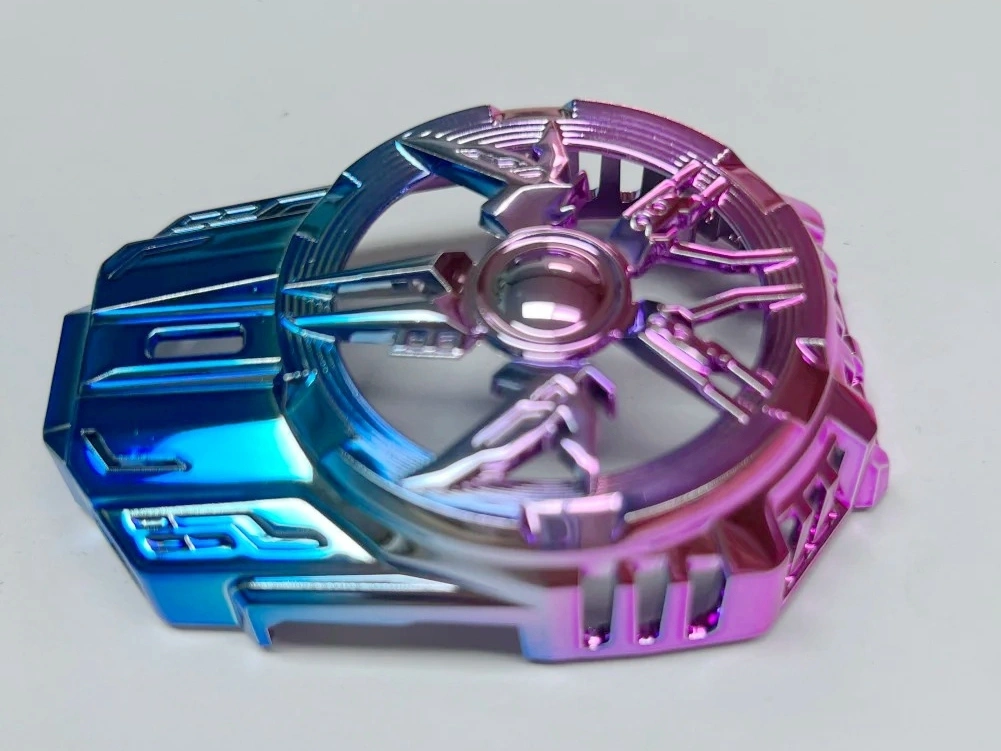
Surface Treatment for Rapid Molding Parts
Neway offers advanced surface treatment for rapid molding parts, including rapid vacuum casting, plastic injection molding, metal injection molding, and ceramic injection molding. Our services enhance durability, finish quality, and performance, ensuring precision and reliability for diverse applications.

Learn More
Thermal Coating

Learn More
As Machined

Learn More
Painting
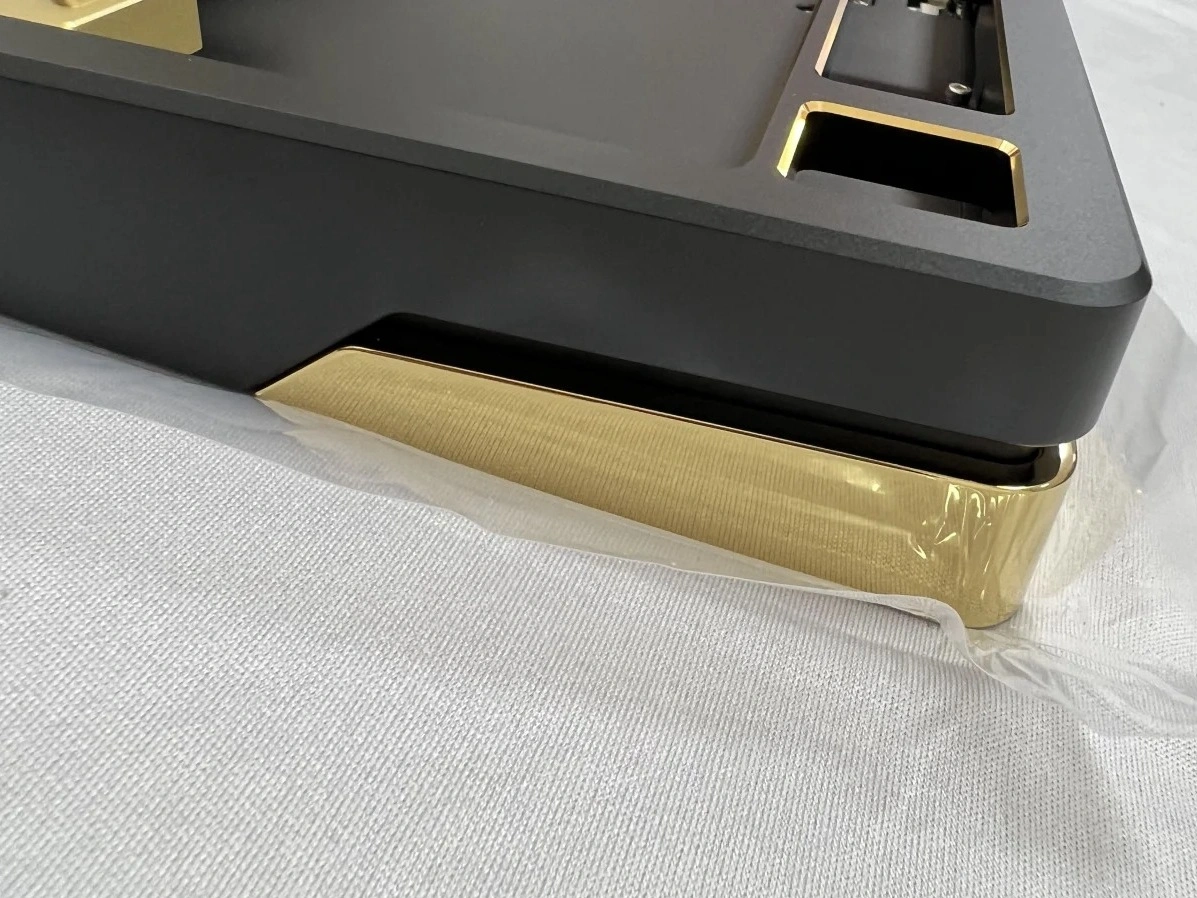

Learn More
PVD (Physical Vapor Deposition)
Learn More
Sandblasting
Learn More
Electroplating
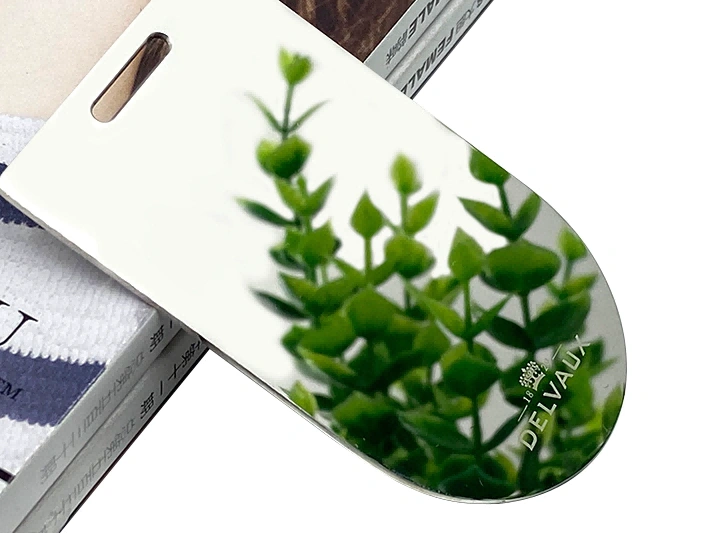

Learn More
Polishing

Learn More
Anodizing

Learn More
Powder Coating

Learn More
Electropolishing

Learn More
Passivation

Learn More
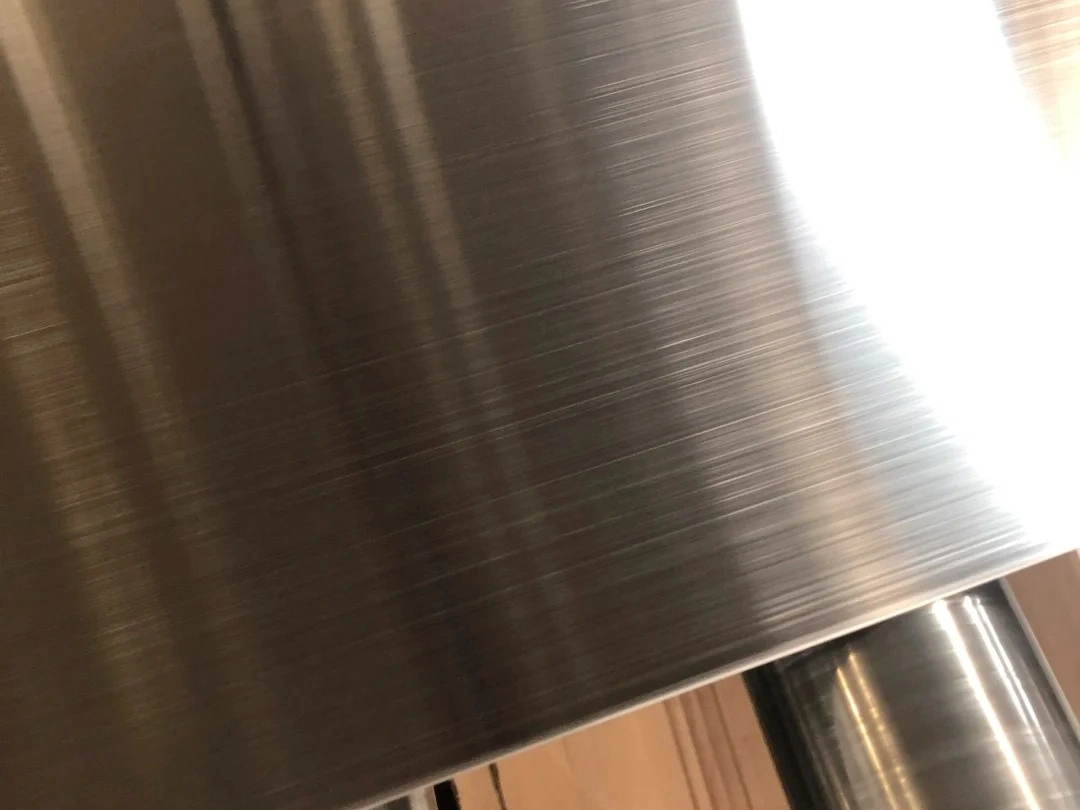
Brushing

Learn More
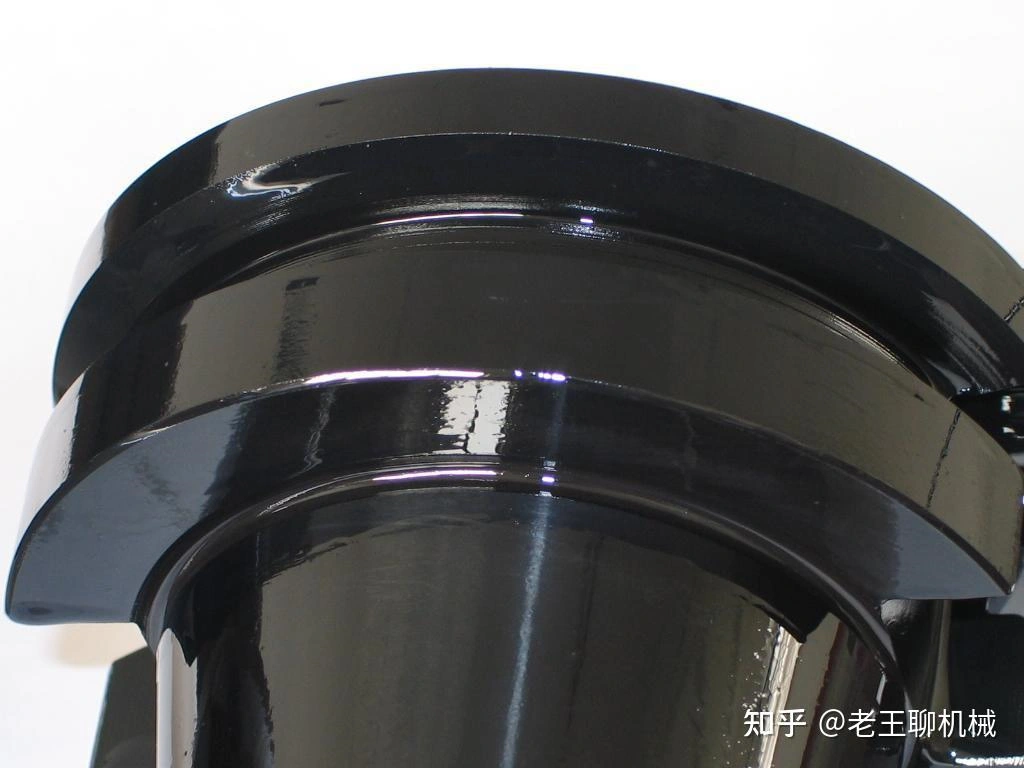
Black Oxide

Learn More
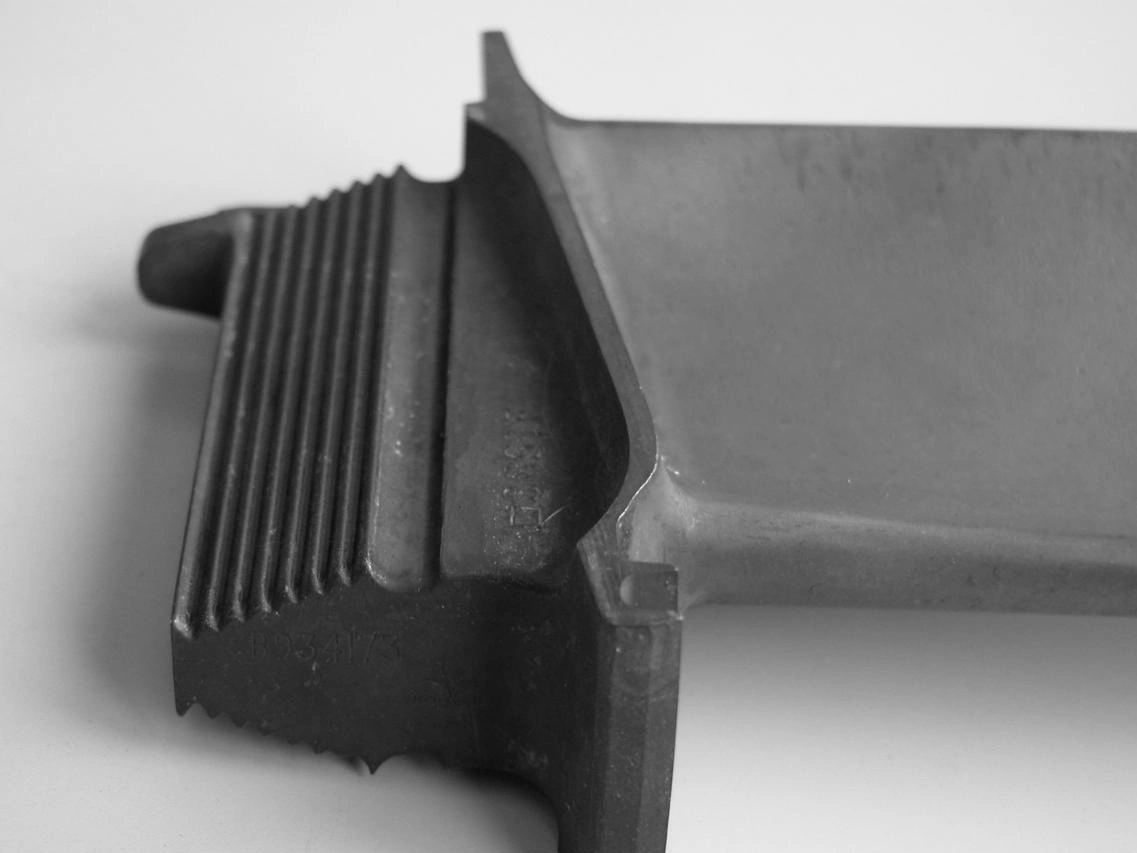
Heat Treatment

Learn More
Thermal Barrier Coating (TBC)

Learn More
Tumbling

Learn More
Alodine

Learn More
Chrome Plating

Learn More
Phosphating
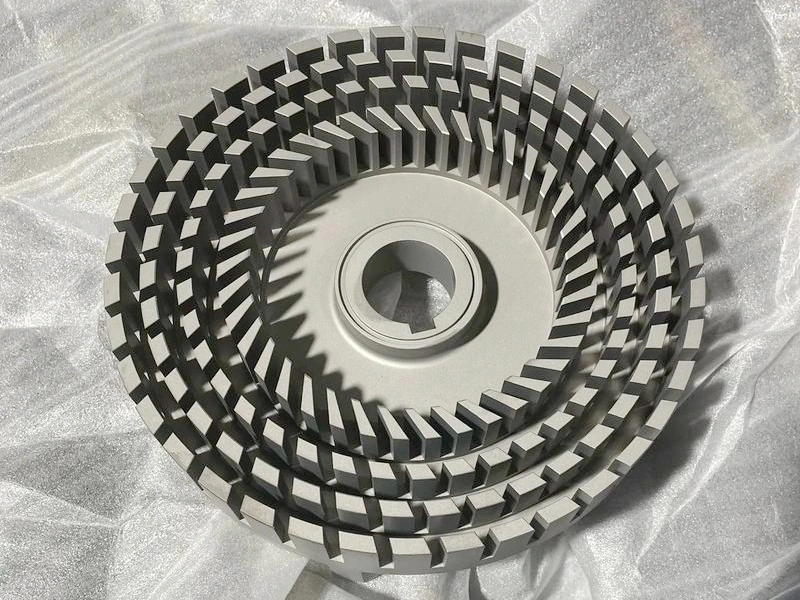

Learn More
Nitriding

Learn More
Galvanizing
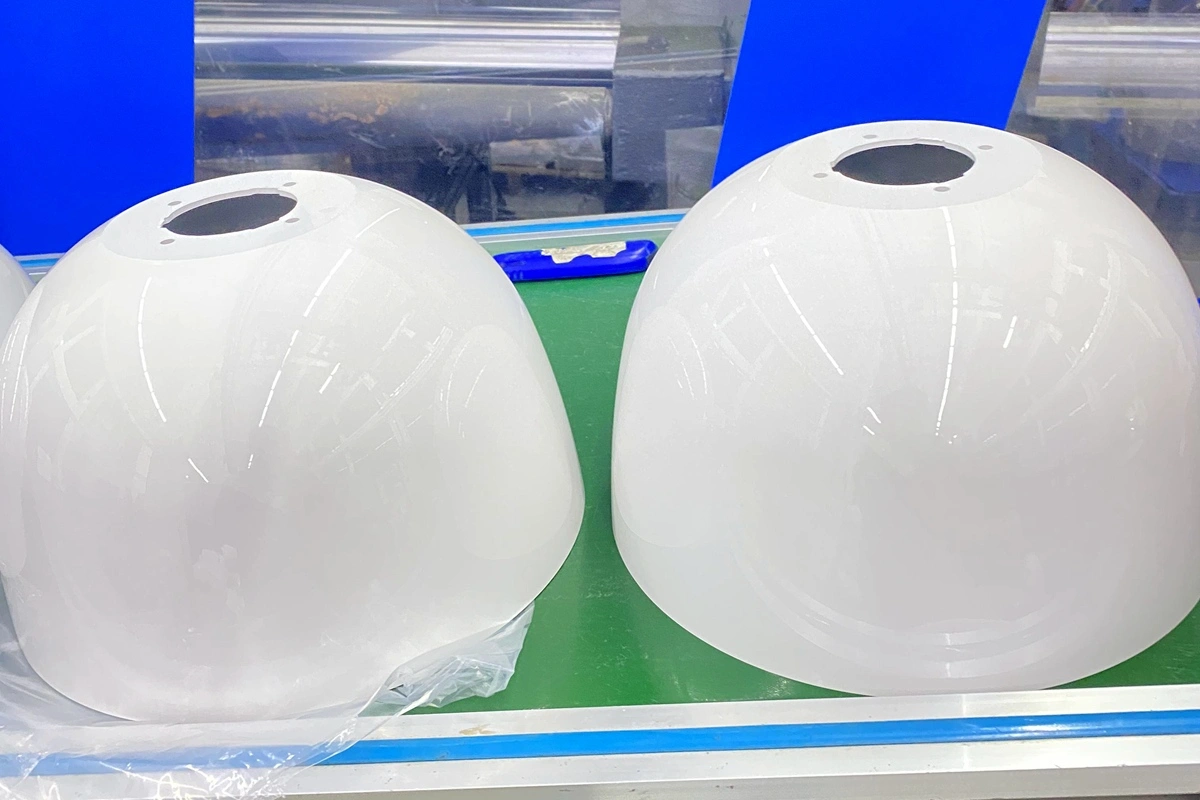

Learn More
UV Coating
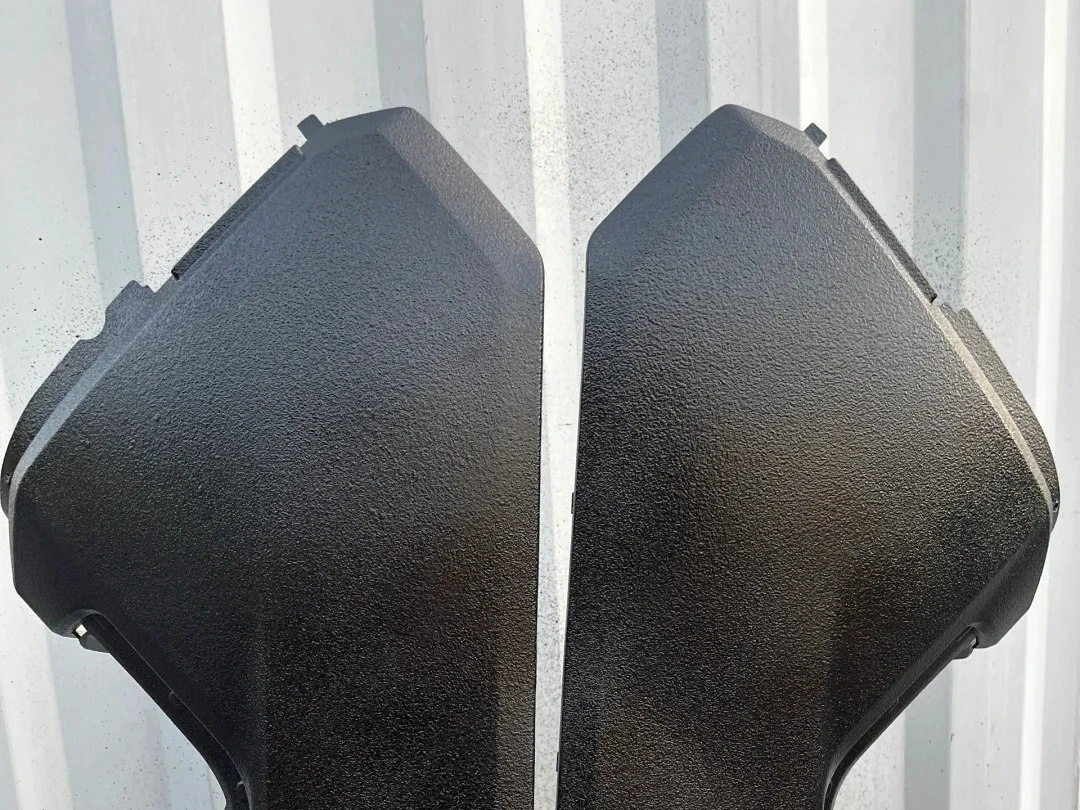

Learn More
Lacquer Coating
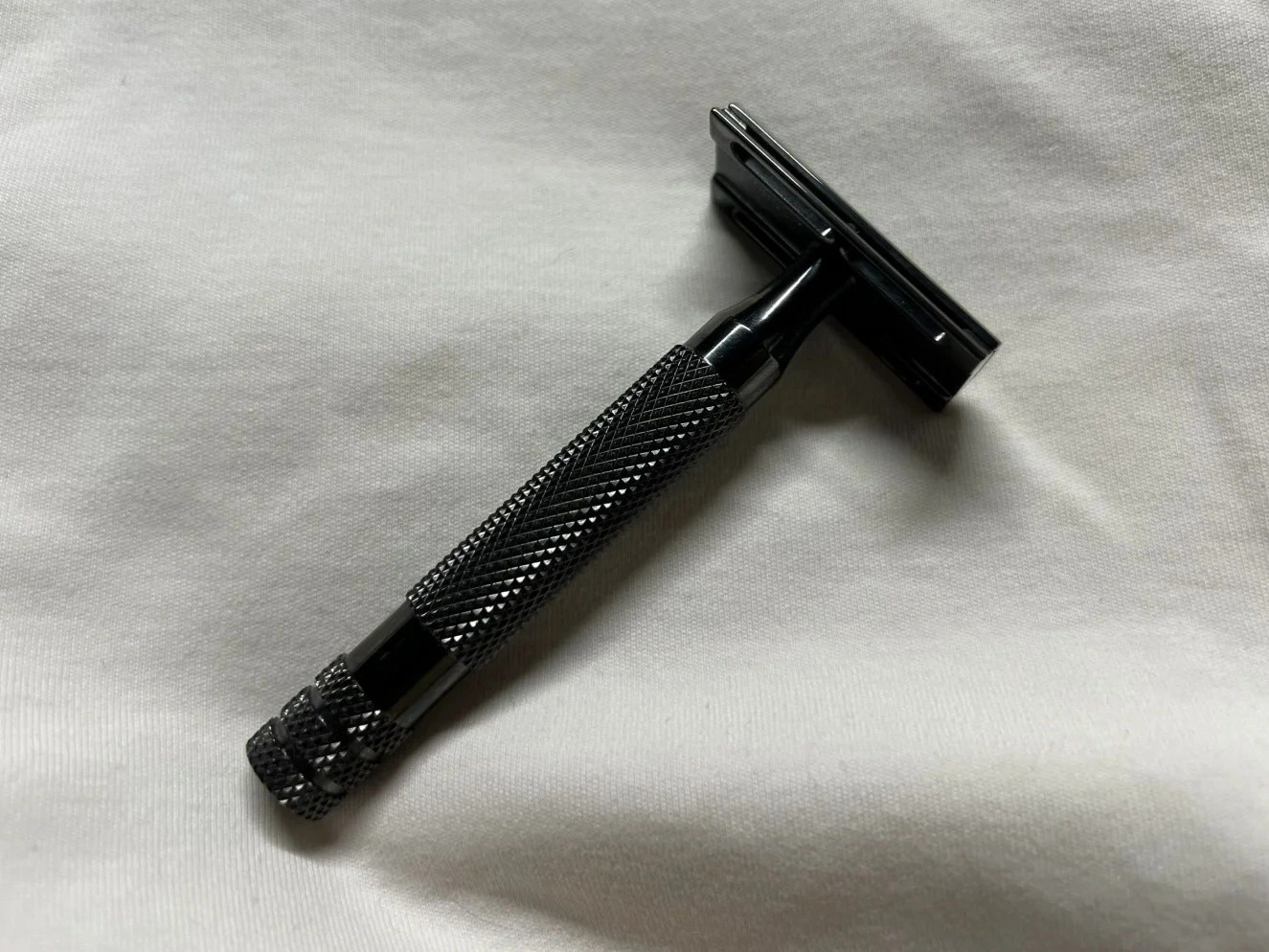

Learn More
Teflon Coating
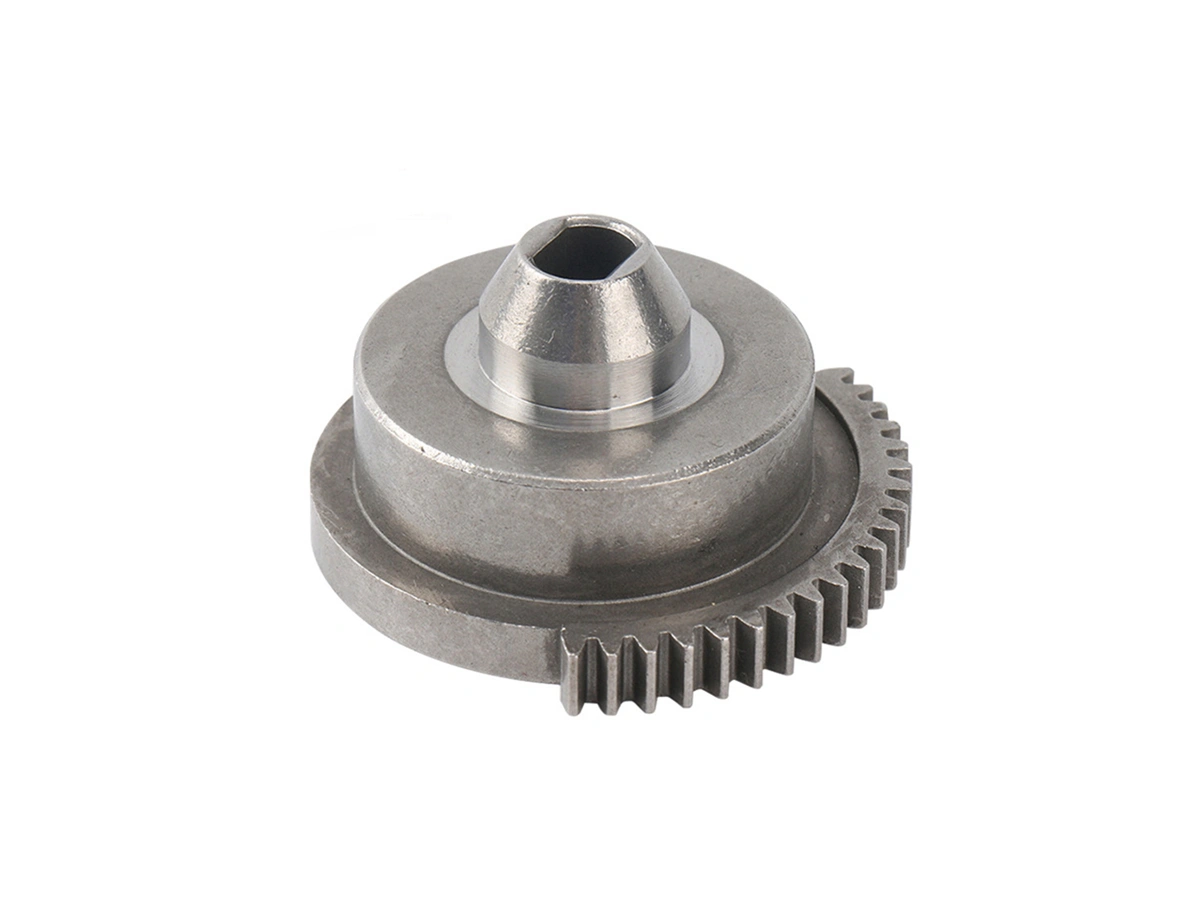
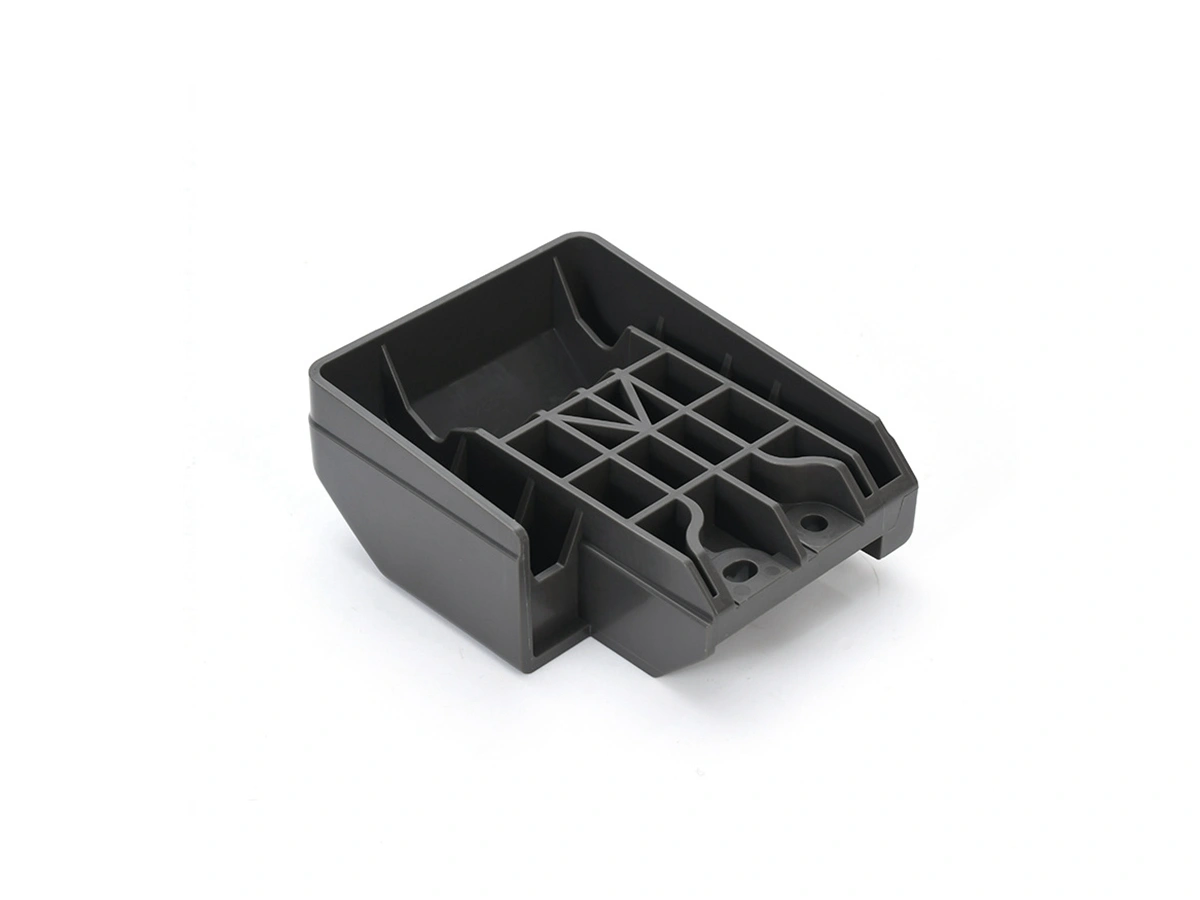
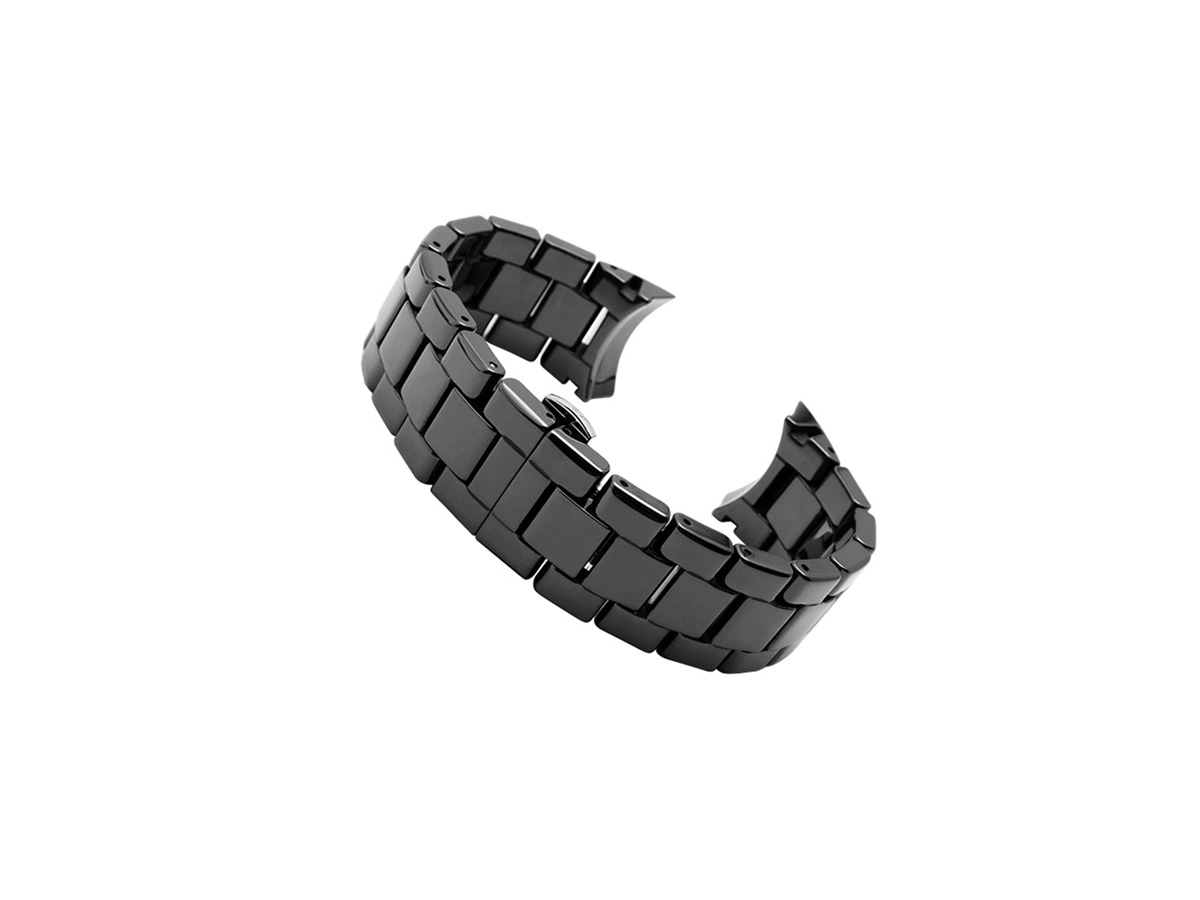
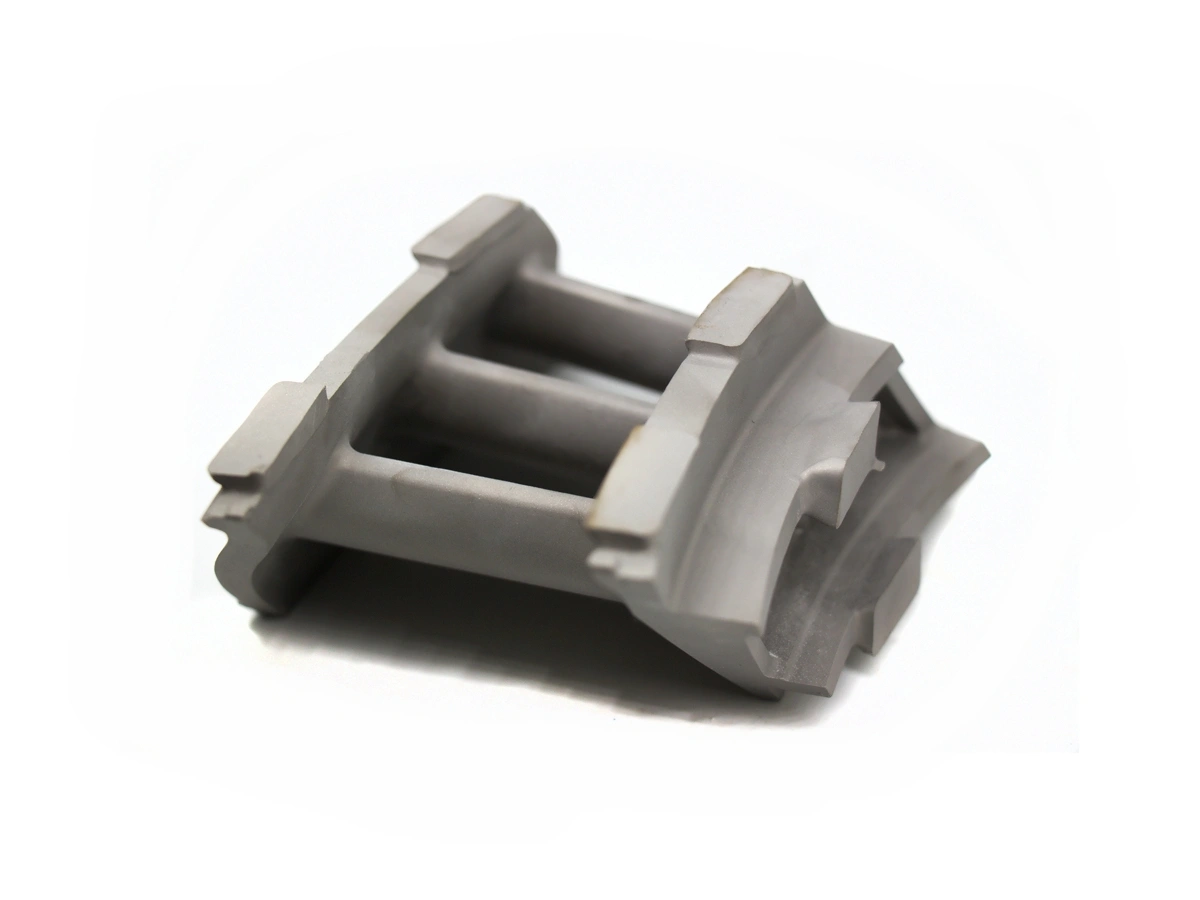
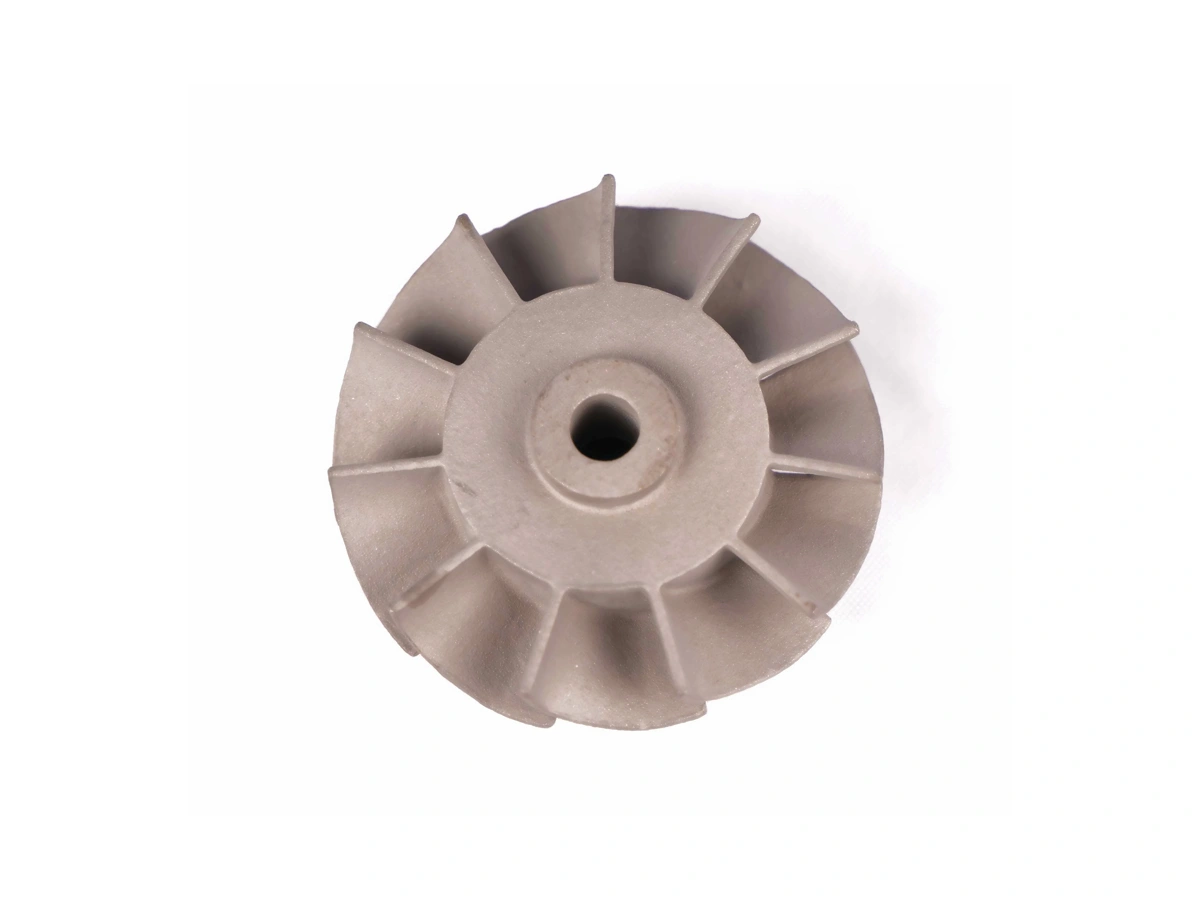
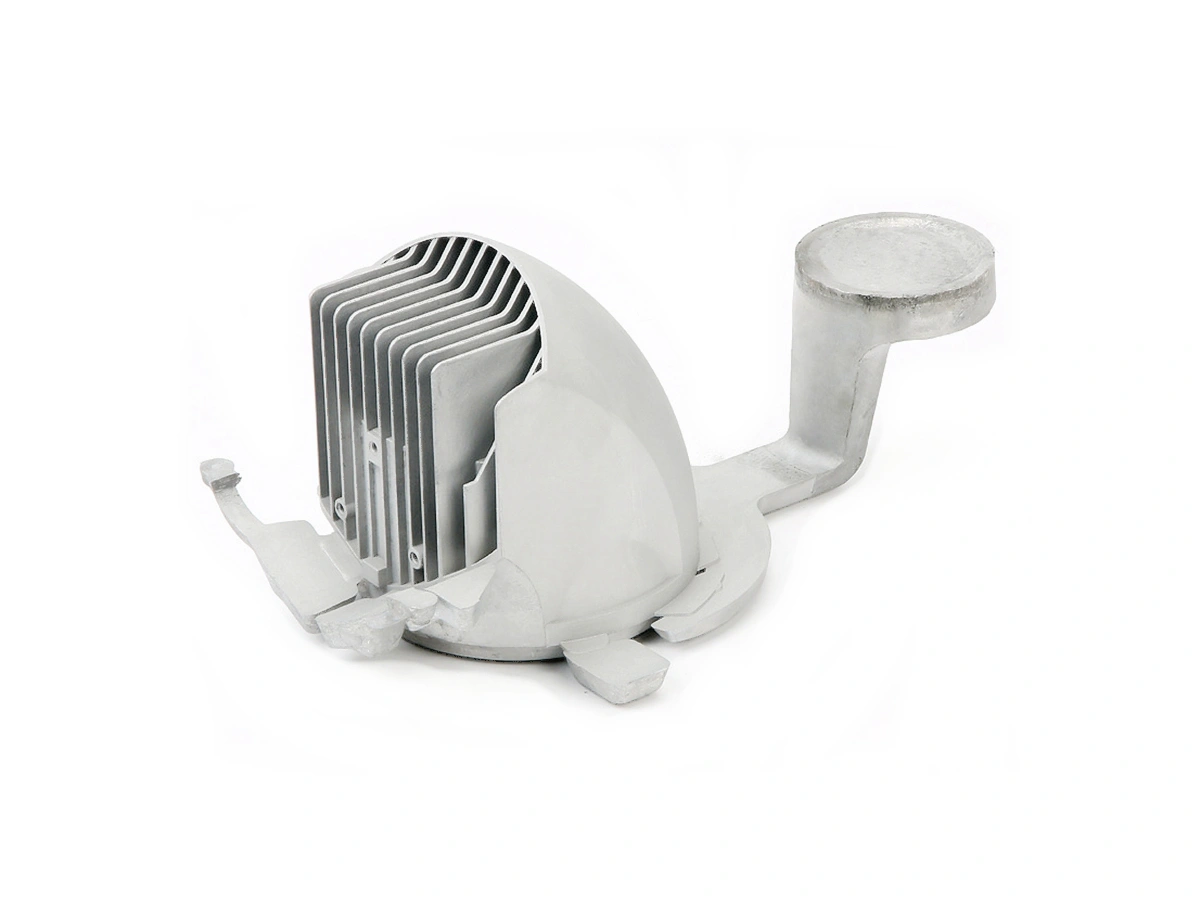
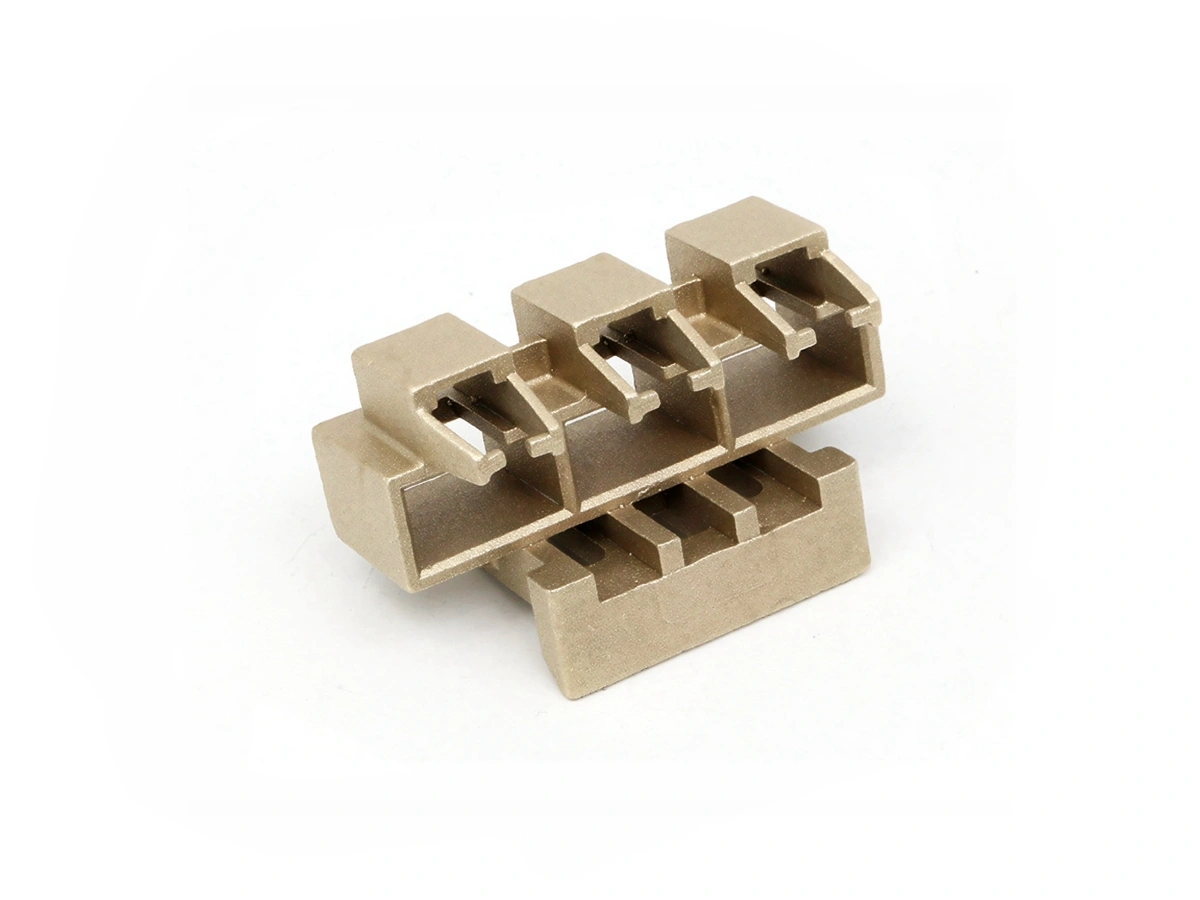
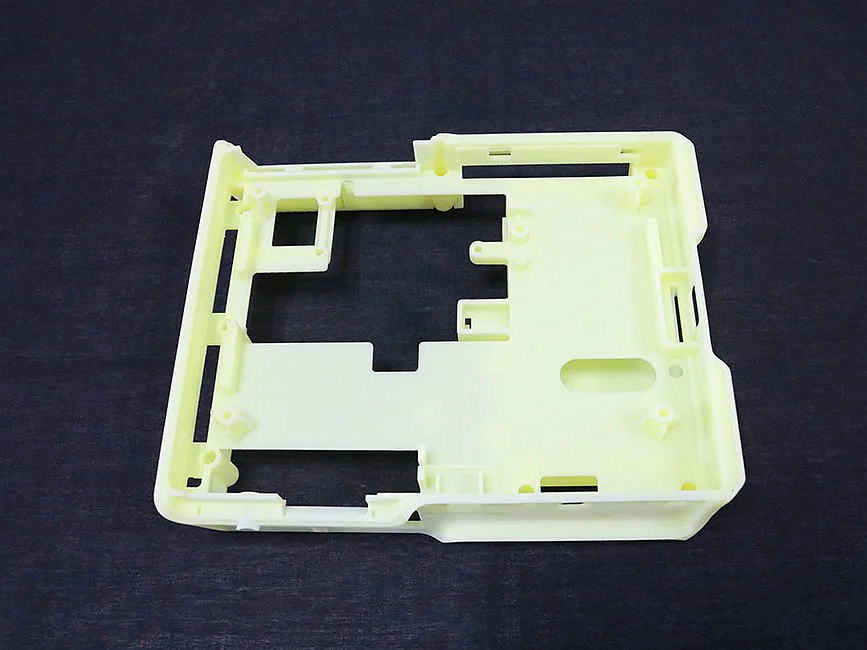
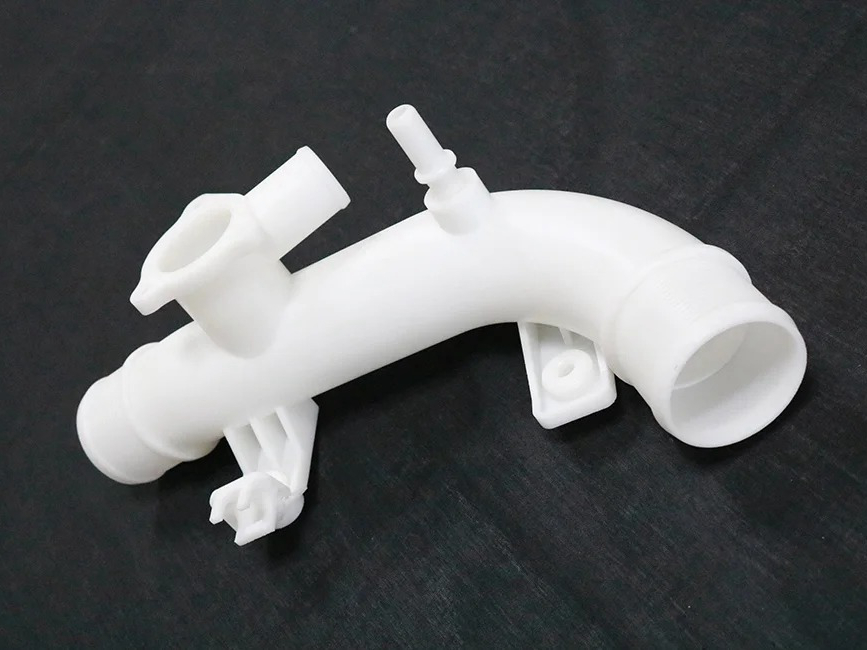
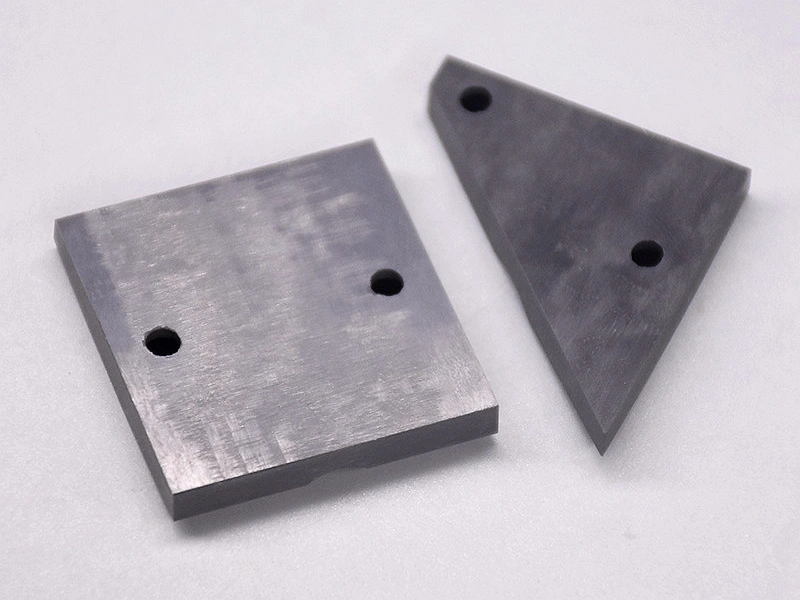
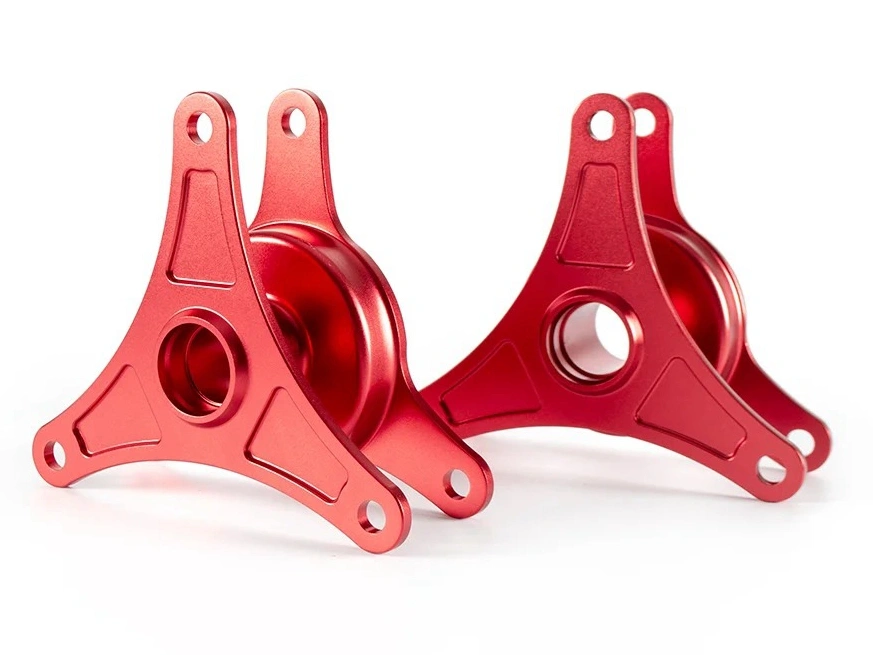
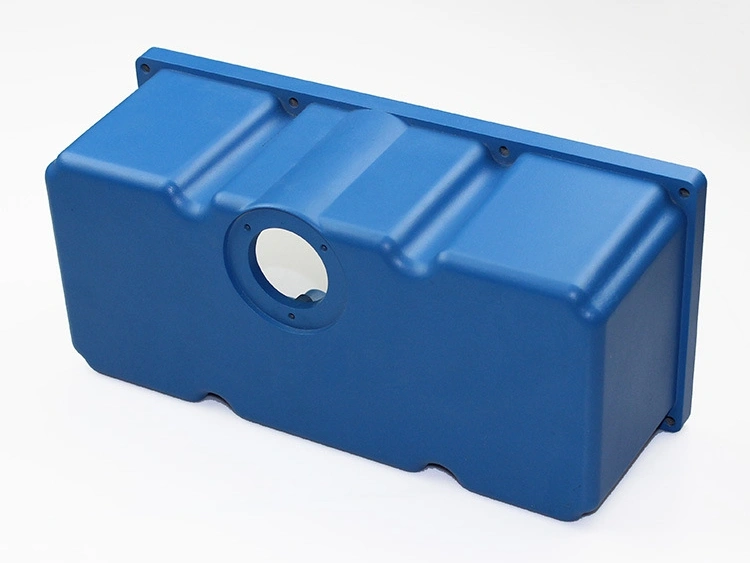
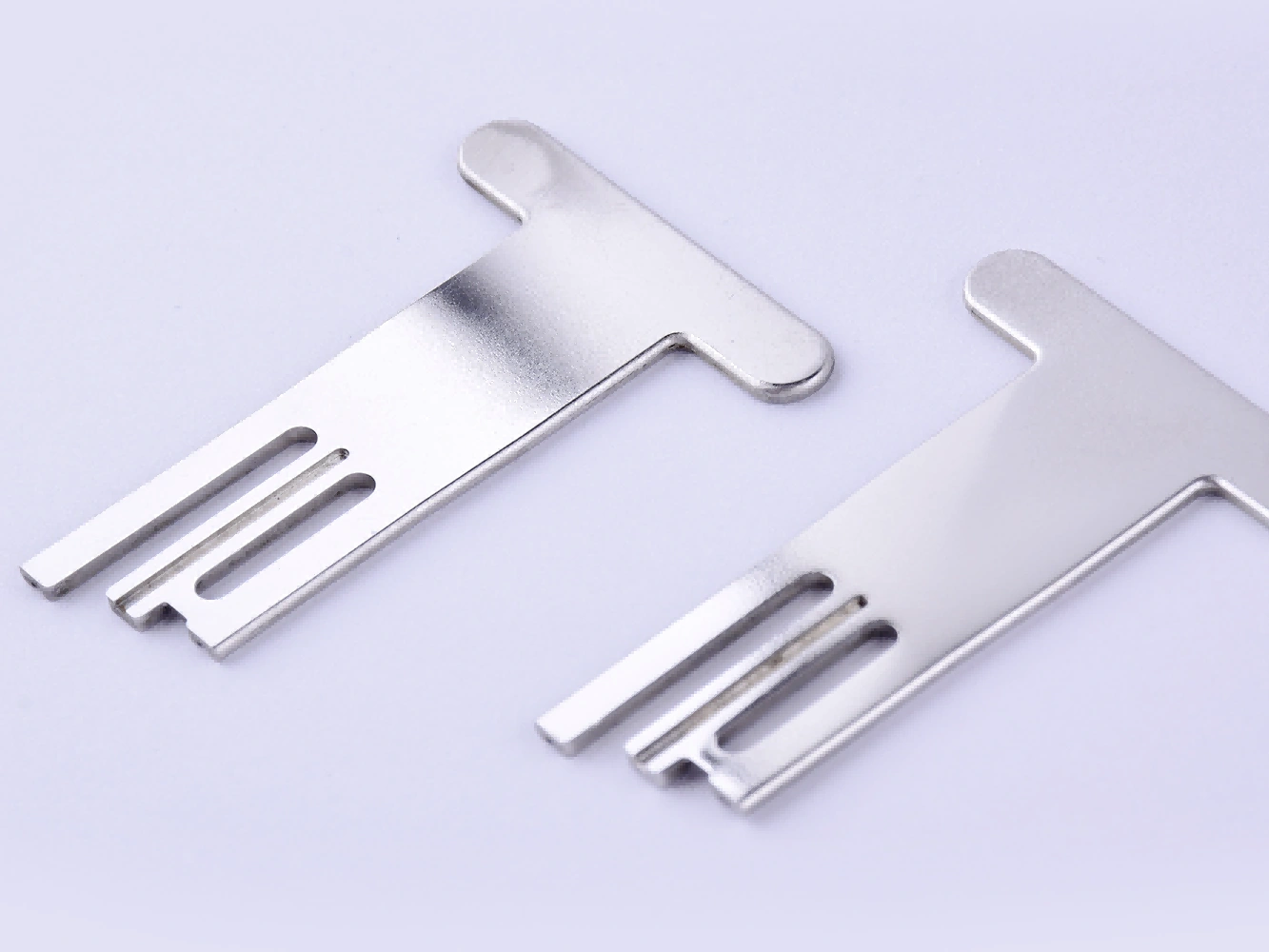
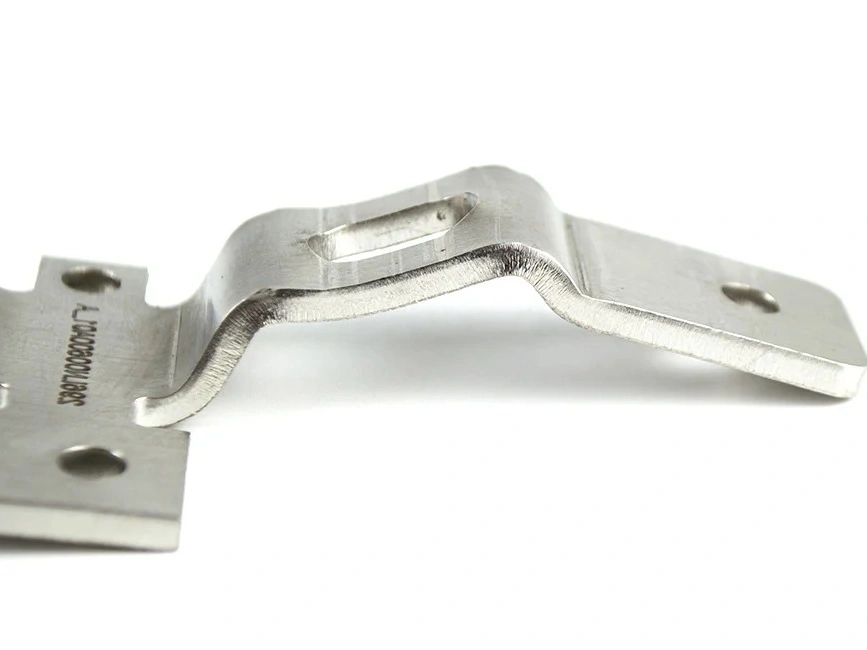
Custom Rapid Molding Parts Case Study
Our custom rapid molding parts case study showcases successful applications using rapid vacuum casting, plastic injection molding, metal injection molding, and ceramic injection molding. We deliver precise, high-quality parts tailored to client needs, optimizing production speed and cost efficiency.
Let's Start A New Project Today
Suggestions for Rapid Molding Parts
For optimal rapid molding parts, consider factors such as a 1-3° draft angle for easy ejection, minimum hole sizes of 0.8mm, tight tolerance control (±0.1mm), uniform wall thickness, proper radii, and material selection based on part performance and application needs.
Frequently Asked Questions
Explore Related Resources
Solutions
Copyright © 2026 Machining Precision Works Ltd.All Rights Reserved.