How do tighter tolerances impact CNC machining costs?
How Do Tighter Tolerances Impact CNC Machining Costs?
Relationship Between Tolerances and Machining Complexity
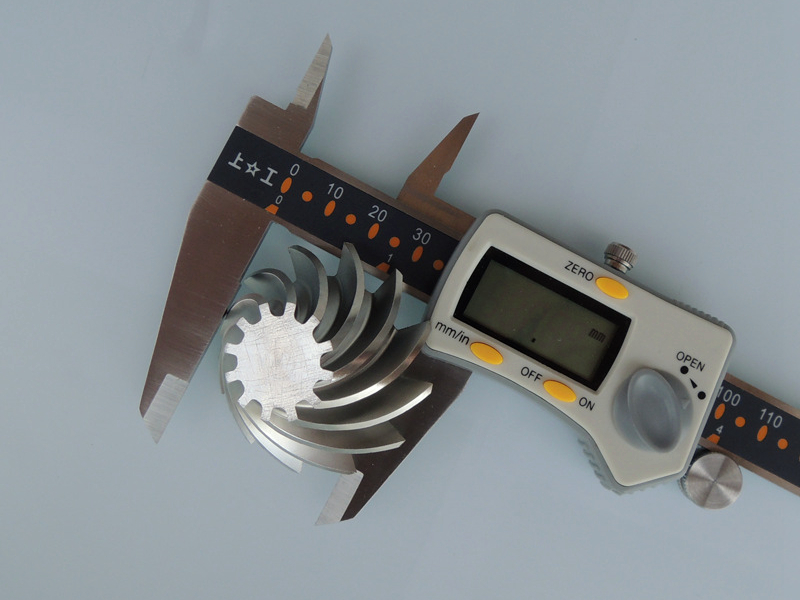
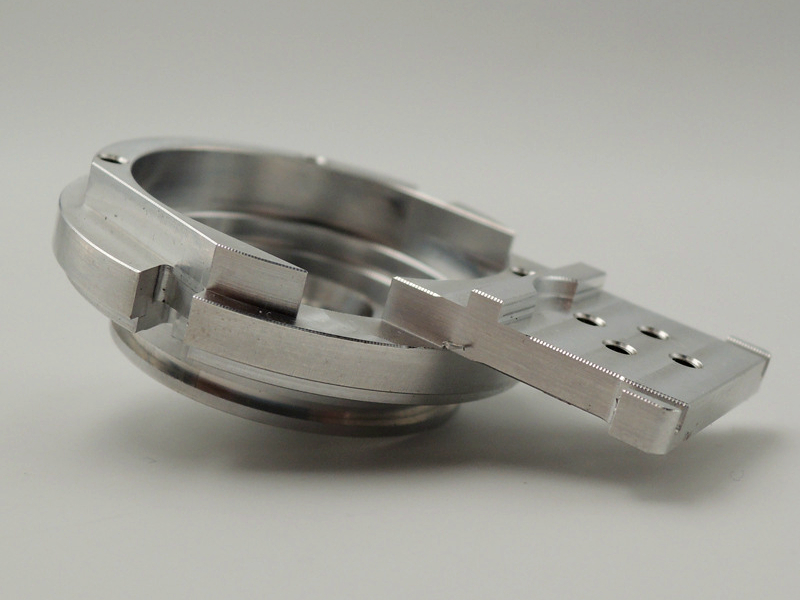
Tighter tolerances significantly influence CNC machining costs by increasing manufacturing complexity, precision requirements, and processing time. Generally, standard machining tolerances range from ±0.1mm to ±0.05mm; however, precision applications often demand tolerances as tight as ±0.01mm or even finer. Achieving such precise specifications necessitates specialized equipment, advanced tooling, and skilled machining operators, all contributing directly to higher production costs.
Factors Driving Cost Increases Due to Tighter Tolerances
Machining Time: High precision demands slower machining speeds, extended cycle times, and multiple finishing passes, raising overall production duration.
Tooling Costs: Achieving tighter tolerances typically requires premium cutting tools or specialized coatings to maintain accuracy and reduce wear.
Inspection and Quality Control: Enhanced precision necessitates rigorous inspection, often involving precision machining techniques, coordinate measuring machines (CMM), or advanced laser scanning, escalating inspection expenses.
Material Waste and Rework: Increased precision heightens the risk of rework or material scrapping, especially when manufacturing complex components or using challenging materials such as superalloys, titanium alloys, or ceramics.
Practical Cost Implications in CNC Machining
For example, shifting from a standard ±0.05mm tolerance to a precision tolerance of ±0.01mm can increase machining costs by approximately 20%–50%, depending on material complexity and part geometry. Industries like aerospace, medical devices, and robotics often justify these additional expenses due to stringent performance and safety standards.
Balancing Precision and Cost Efficiency at Neway
At Neway, we balance precision and cost-efficiency by leveraging advanced multi-axis machining, expert tooling strategies, and rigorous quality assurance protocols. Our engineers collaborate closely with clients, recommending optimal tolerances that fulfill technical requirements while controlling manufacturing costs effectively.
Explore more about our precision machining capabilities: